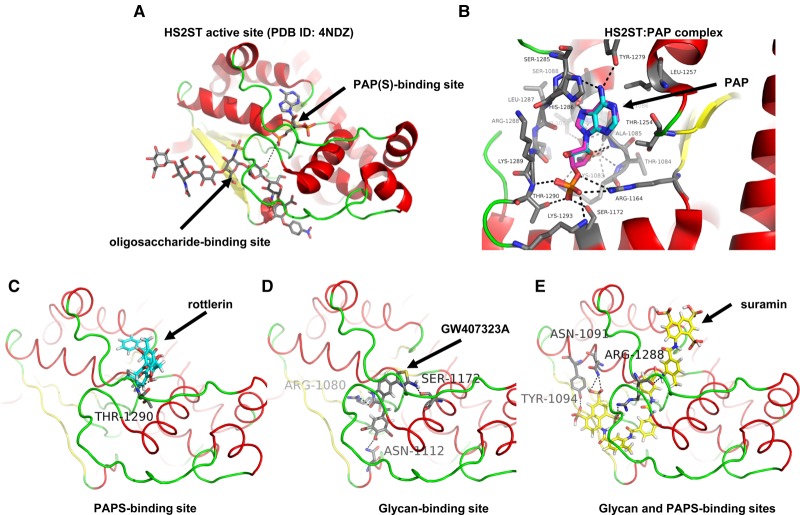
Figure 5. Molecular docking analysis of HS2ST with small-molecule inhibitor compounds.
(A) Structural representation of the catalytic domain of chicken MBP-HS2ST crystallised with bound heptasaccharide and non-sulfated PAP cofactor (protein rendered as a cartoon). Red — α-helix, yellow — β-sheet, green — loop. PAP (adenosine-3′-5′-diphosphate) and heptasaccharride are rendered as coloured sticks. Grey — carbon, red — oxygen, blue — nitrogen, yellow — sulfur. Black dotted line indicates close proximity of glycan 2-OH group and PAP. (B) Structure of HS2ST with near-identical crystallographic (carbons in cyan) and docking (carbons in purple) poses of PAP (protein rendered as a cartoon). Red — α-helix, yellow – β-sheet, green — loop. PAP rendered as coloured sticks. Cyan/grey/purple — carbon, red — oxygen, blue — nitrogen, dark yellow — sulfur). Black dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. Molecular docking of (C) rottlerin and (D) the indole RAF inhibitor GW407323A or (E) suramin into the HS2ST catalytic domain (protein depicted as a cartoon). Red — α-helix, yellow — β-sheet, green — loop. Docked molecules coloured as sticks. Pink/yellow/salmon/grey — carbon, red — oxygen, blue — nitrogen, dark yellow — sulfur, white — hydrogen). Black dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds. Amino acid numbering corresponds to that of trimeric HS2ST.