Figure 1.
Identification and In Vitro Pharmacodynamic Characterization of Aptamers with Higher hTLR4 Binding Affinity
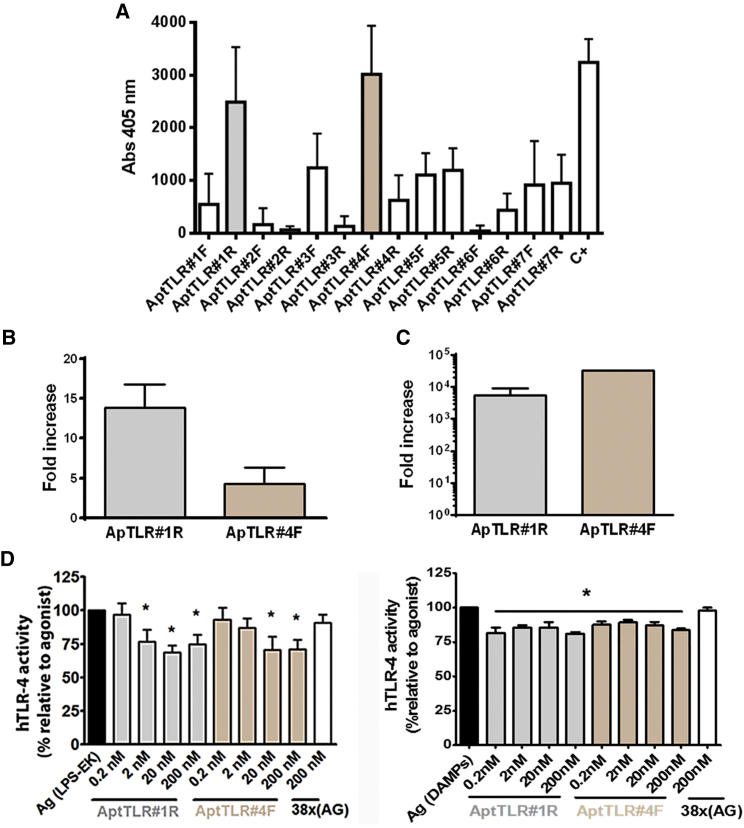
(A) Graph showing binding of the selected aptamers to hTLR4 in ELONA assays. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Fold increase aptamer recovery after incubation of resin-hTLR4-protein complexes with ApTLR#1R and ApTLR#4F relative to RND40 (n = 3) by qPCR. (C) Fold increase aptamer recovery after incubation of 293-hTLR4A cells with ApTLR#1R and ApTLR#4F relative to HEK293 (n = 3) by qPCR. (D) SEAP assay for the characterization of the antagonistic effect of ApTLR#1R and ApTLR#4F on hTLR4. HB-hTLR4 cells were exposed to LPS (0.1 ng/mL; left) or DAMPs (5 μL; right) 1 hr prior to the addition of aptamers (0.2–200 nM) to the medium. Data are expressed as the percentage of SEAP activity relative to LPS or DAMPs alone (agonist control) (n = 9). Student’s t test (*p < 0.05 versus agonist control).