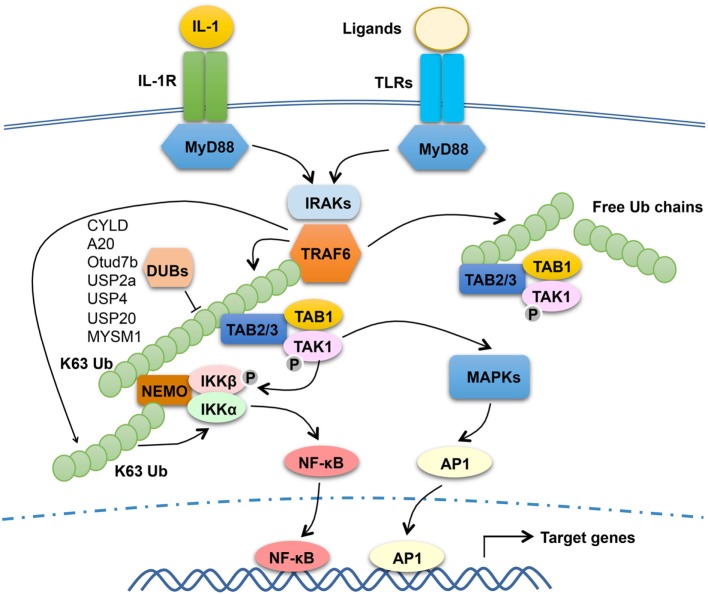
Figure 1.
The function and regulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6 in MyD88 signaling pathway. Upon stimulation with IL-1 or toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands, MyD88 recruits IL-1R-associated kinases (IRAKs) (including IRAK1, IRAK2, and IRAK4) and TRAF6 to assemble a MyD88 signaling complex. Once activated in the MyD88 complex, TRAF6 functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that catalyzes the synthesis of K63-linked polyubiquitin chains conjugated to itself or NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) or existing as free ubiquitin chains. The self-ubiquitinated TRAF6 recruits the ubiquitin-dependent kinase transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and its downstream kinase IκB kinase (IKK) to assemble a signaling complex that facilitates TAK1 and IKK activation. This process requires the TAK1 regulatory subunit TAB 2 (or TAB 3) and the IKK regulatory subunit NEMO, both have ubiquitin-binding functions. Activated TAK1 mediates activation of IKK and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which further activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) (RelA- and c-Rel-containing complexes) and AP1. TRAF6 mediated NEMO ubiquitination also contributes to the activation of IKK and NF-κB. Several DUBs have been shown to negatively regulate TRAF6 function through deconjugation of its K63 polyubiquitin chains.