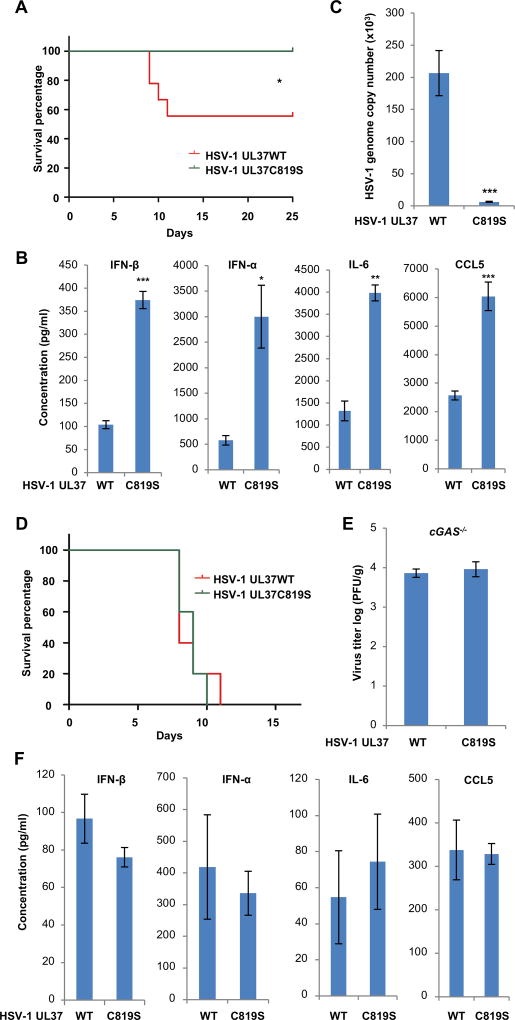
Figure 1. HSV-1 carrying deamidase-deficient UL37C718S more robustly induces cytokine production than wild-type HSV-1 in vivo.
(A–C) Age- and gender-matched BL6 mice were infected with HSV-1 UL37 wild-type (WT) or HSV-1 UL37C819S (C819S) (5 × 107 PFU). (A) Mouse survival was recorded and shown in percentage over time (n=9). (B) Blood was collected at 8 hours post-infection (hpi) and indicated cytokines in sera were determined by ELISA (n=5). (C) Mice were sacrificed at 3 days post-infection (dpi) and the viral genome copy number in the brain was determined by real-time PCR analysis (n=5).
(D–F) cGAS−/− mice were infected with HSV-1 UL37 wild-type (WT) or HSV-1 UL37C819S (UL37C819S) (5 × 107 PFU). (D) Mouse survival was recorded over time (n=10). (E) Virus titer in the brain (at 3 dpi) and (F) cytokines in the sera (at 8 hpi) were determined (n=5) by plaque assay and ELISA, respectively.
Each value is the mean + s.d. of the results of three independent experiments (B, C, E, F). Statistical analysis was performed by log-rank test for (A, D) and unpaired t-test for (B, C, E, F); *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments (A and D).
See also Figure S1.