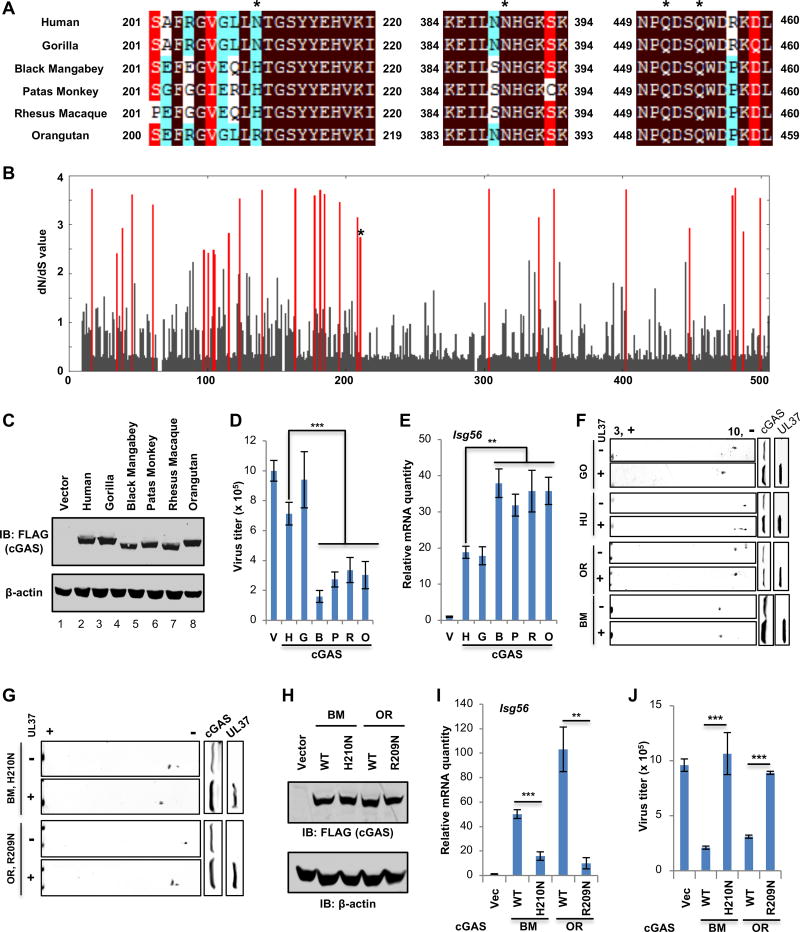
Figure 7. Species-specific deamidation of cGAS promotes HSV-1 lytic replication.
(A) cGAS proteins of human and 5 different nonhuman primate species were aligned, with sequences flanking the four deamidation sites (asterisks) shown.
(B) Starting with an alignment of cGAS from 29 primate species, dN/dS values of each amino acid of cGAS were calculated. The dN/dS value (Y axis) is shown for each codon along the length of the cGAS gene (X axis). Amino acid sites with statistically significant elevation of dN/dS > 1 (PP > 0.5) values are indicated by red lines. The asterisk denotes N210 of human cGAS.
(C–E) cGAS−/− L929 cells were “reconstituted” with human and nonhuman primate cGASs. (C) Whole cell lysates (WCLs) were analyzed by immunoblotting. (D) Cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI=0.01), virus titer in the medium at 24 hours post-infection (hpi) was determined by plaque assay. (E) the expression of Isg56 was analyzed by real-time PCR.
(F) Plasmids containing cGAS of human and nonhuman primates, without or with that containing UL37, were transfected into 293T cells. WCLs were analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting.
(G) Transfection of 293T cells with plasmids containing black mangabey (BM) or orangutan (OR) cGAS with the H210N or R209N mutation and that containing UL37, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting were carried out as in (F).
(H–J) cGAS−/− L929 cells were “reconstituted” with black mangabey (BM) or orangutan (OR) cGAS or that containing H210N or R209N. (H) WCLs were analyzed by immunoblotting. (I) Cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI=0.01), virus titer in the medium was determined. (J) Cells were infected with HSV-1 at MOI=5. The expression of Isg56 was analyzed by real-time PCR.
Each value is the mean + s.d. of the results of three independent experiments (D, E, I, J). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired t-test for (D, E, I, J); **P<0.01, ***P<0.005. Data are representative of three independent experiments (C, F, G, H).
See also Figure S8 and S9.