Figure 1.
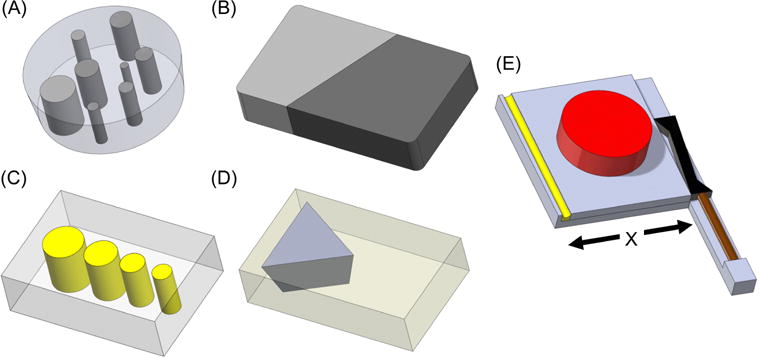
Rendered images of the four phantoms and motion actuator. (A) One layer (out of three) of the stiffness contrast-detail phantom with cylindrical inclusions of varying diameters and varying silicone composition (Table 1). (B) Stiffness interface phantom with 100% silicone A341 gel on left (light gray) and 70% silicone A341 gel on right (dark gray). (C) Damping ratio inclusion phantom with soft tofu background (gray) and 0.75% agar inclusions of varying diameters (yellow). (D) Damping ratio interface phantom with 0.65% agar background (yellow) and soft tofu (gray). (E) Motion actuator with a stack piezoelectric actuator (brown), lever (black), actuation plate (gray), phantom (red), and spring (yellow). The spring ensures constant contact of the actuation plate with the lever enabling shearing motion along the “X” direction.
