Fig. 2 .
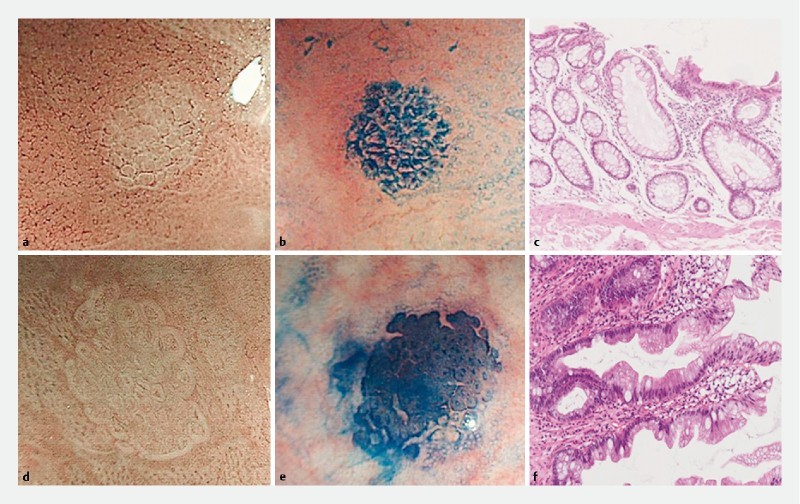
Endoscopic findings of aberrant crypt foci (ACF) using narrow-band imaging (NBI) and methylene blue, and histological findings. a – c Representative images of non-dysplastic ACF. a One focus that consists of large crypts with a regularly arranged white pericryptal zone under NBI magnification. b Methylene blue staining of this focus revealed that the large crypts had a thicker epithelial lining and a larger pericryptal zone than normal crypts. c Histologically, there was enlargement and elongation of the ducts, but not dysplasia (orig. mag. × 10). d – f Representative images of dysplastic ACF. d One focus consisted of large crypts with a white pericryptal zone, but the border of each crypt was indistinct or invisible. e Methylene blue staining revealed that the epithelial lining was thicker than in non-dysplastic ACF, and the crypt lumen was compressed or unclear. f Histologically, there were hyperchromatic nuclei with stratification, and loss of polarity (orig. mag. × 10).
