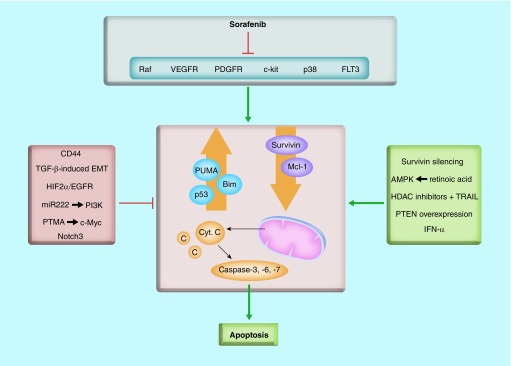
Figure 4. . Different pathways converge in promotion or inhibition of sorafenib-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sorafenib has been described as apoptosis-inducer in HCC cells, through upregulation of the proapoptotic PUMA and BIM, downregulation of the antiapoptotic Mcl-1 and Survivin, activation of BAX and BAK, release of cytochrome c and increase in caspase-3 activity. Different pathways and molecules have been shown to regulate sorafenib effects in hepatocytes, having either an inhibitor or an activator role. See text for further details.