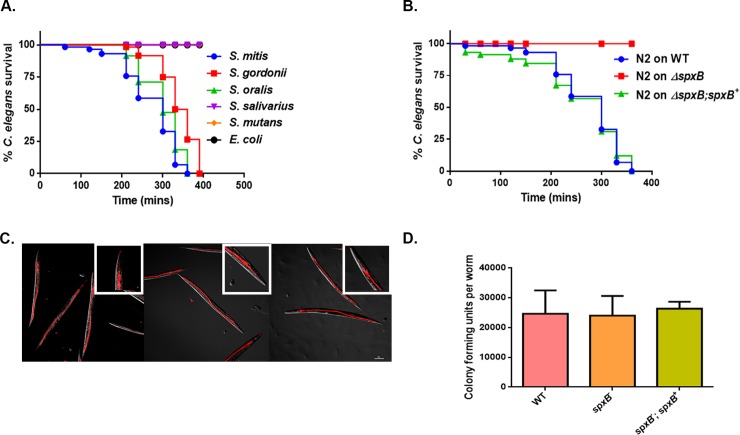
Fig 1. H2O2 mediated killing of C. elegans by mitis group streptococci.
(A) Survival of N2 L4 larvae exposed to S. gordonii, S. oralis, S. mitis, S. salivarius S. mutans and E. coli OP50 on THY plates. (B) Survival of S. gordonii WT, ΔspxB mutant and ΔspxB;spxB+ complemented strains on N2 L4 larvae containing THY plates. The data are representative of experiments repeated two or more times with an n = 60–90 worms for each condition. Kaplan-Meier log rank analysis was used to compare survival curves and to calculate the median survival. P-values <0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. (C) Fluorescently labelled WT, ΔspxB mutant and ΔspxB;spxB+ complemented strains of S. gordonii were exposed to L4 larvae for 2 hours and visualized by confocal microscopy. The streptococcal strains are labelled in red and are located within the intestinal lumen of the worms. Close-ups are shown in the upper right-hand corner of each image. No difference was observed in the levels of colonization in the worms between the strains. The experiment was repeated three times. (D) No significant difference in intestinal accumulation of WT, ΔspxB mutant and ΔspxB;spxB+ complemented strains were observed in L4 worms following a 2 hour exposure. The experiment was repeated 3 times and a total of 25 worms were disrupted for each strain of bacteria.