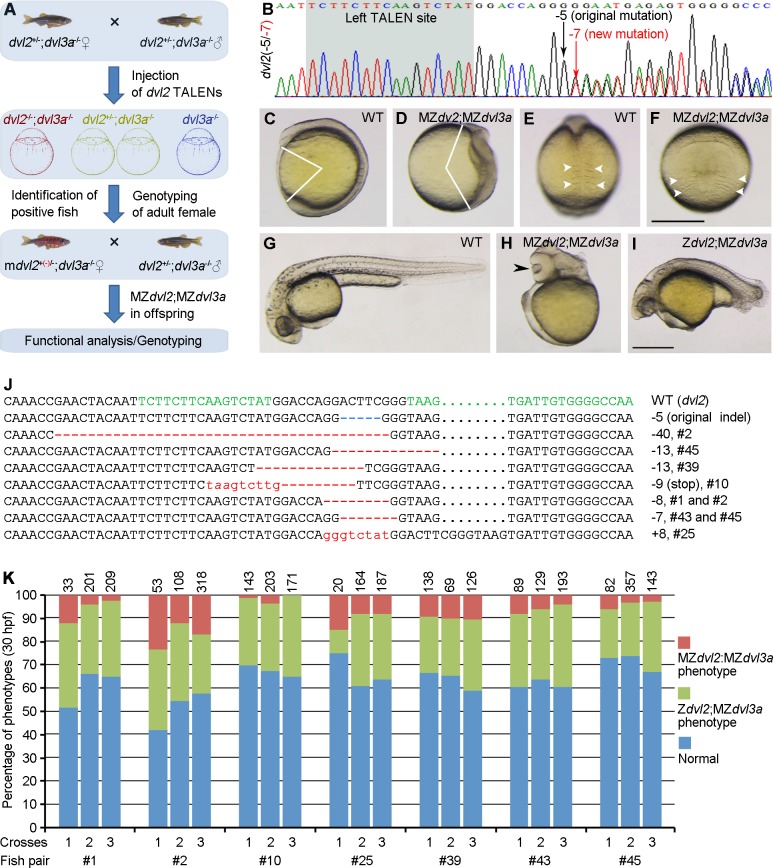
Fig 4. Analysis of MZdvl2;MZdvl3a mutants.
(A) Schema illustrating the strategy to generate female mosaic mdvl2+(-)/-;dvl3a-/- adult fish with a new mutant allele (red) in dvl2. MZdvl2;MZdvl3a mutant embryos are present at varied proportions in the offspring from crosses between female mdvl2+(-)/-;dvl3a-/- and male dvl2+/-;dvl3a-/- fish, depending on the efficiency of germline mutations in the remaining dvl2 WT allele. (B) An example of the sequencing chromatogram with both the original mutant allele and a new indel in dvl2 locus. (C-F) Lateral (C, D) and dorsal (E, F) views of a representative WT embryo (C, E), and an MZdvl2;MZdvl3a mutant (D, F) at 11.5 hpf. Notice that the mutant embryo displays most severely impaired AP axis and convergence of paraxial mesoderm, with strongly widened somites (arrowheads). (G) A WT embryo at 30 hpf. (H) Lateral view of a representative MZdvl2;MZdvl3a mutant at 30 hpf shows deficiency of trunk and posterior regions, and cyclopia (arrowhead; see also S12 Fig). (I) The phenotype of a Zdvl2;MZdvl3a mutant with characteristic caudal truncation at 30 hpf. (J) Genotyping of dvl2 alleles in MZdvl2;MZdvl3a mutant embryos from 7 independent fish pairs. A novel indel (red) along with the original mutation (blue) are present in the mutants. The left and right TALEN targeting sites are indicated in green. Dots are introduced to optimize sequence alignment. (K) Quantitative analyses of the occurrence of MZdvl2;MZdvl3a and Zdvl2;MZdvl3a mutants among offspring from 7 independent fish pairs. Each fish pair was crossed three times, and numbers on the top of each column indicate total embryos scored. Scale bar: (C-F) 400 μm; (G-I) 400 μm.