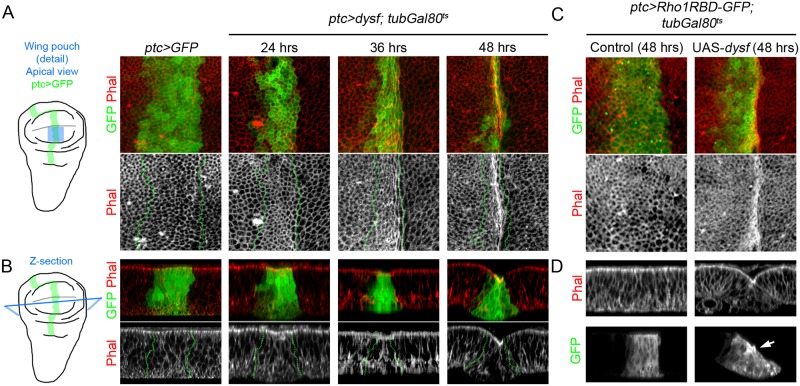
Fig 6. Ectopic expression of dysf induces fold formation and Rho1 activation.
(A-D) Apical view (A and C) and Z-section (B and D) of a region of the wing pouch (blue square in the schematic wing disc). The ptc-Gal4 driver is used to express different UAS constructs in a band of cells of the anterior compartment of the wing pouch. Control ptc>GFP (A and B) or ptc>Rho1RBD-GFP (C and D) and different time points of ptc>dysf expression, using the tubulin-Gal80ts system. The ptc domain is marked with GFP (green and dotted lines). Phal is in red and separate grey channel where indicated. (A) The dysf-expressing cells undergo apical constriction and consequently the ptc domain becomes narrower. By 48 hrs, accumulation of F-actin is clearly visible. (B) Z-sections of the genotypes and time points described above. Note the progressive narrowing of the GFP positive cells in their apical region and the formation of a fold that is visible by 48h. (C) The ptc>Rho1RBD-GFP cells undergo apical constriction and accumulate F-actin after 48 hrs of dysf expression. (D) Note that the formation of the ectopic fold in ptc>dysf wing pouch is accompanied by an apical accumulation of F-actin and enhanced Rho1 activity in the apical region of the cells that undergo apical constriction.