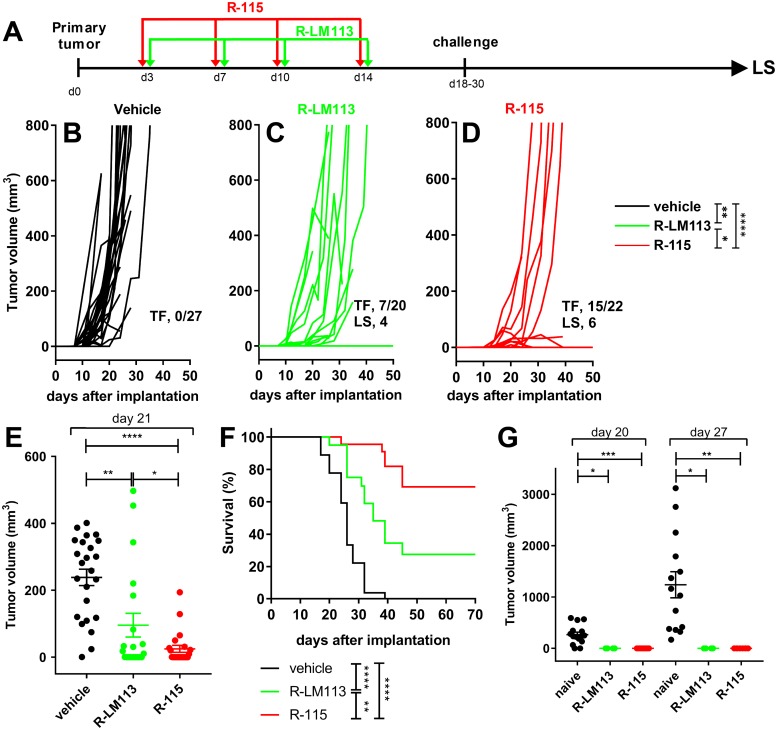
Fig 3. Efficacy of R-LM113 and R-115 administered early after tumor implantation on the growth of HER2-LLC1 tumors.
(A) Schedule of the treatments. The HER2-transgenic/tolerant mice, implanted with HER2-LLC1 cells, received four loco-regional injections of R-LM113, R-115, or vehicle, at 3–4 days distance, starting at d 3 after tumor implantation. At d 18 or 30, mice received a 1° contralateral challenge tumor. The mice which survived the primary tumor were all resistant to the 1° contralateral challenge tumor; a fraction of them was subsequently analyzed as long survivors (LS) (see, Fig 5). (B-D) Kinetics of tumor growth in mice treated with vehicle (B), R-LM113 (C), R-115 (D). Pooled results from 3 experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using the RM (repeated measures) two way ANOVA-test (until d 21). The figures in panels B-D denote the numbers of tumor free/treated mice (TF), and the mice subsequently analyzed as LS. (E) Volumes of the primary tumors at d 21 after implantation. Statistical significance was calculated using the t-test. (F) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the three groups of mice. Statistical significance was calculated using the Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Of note, some tumor free mice were sacrificed during the course of the experiment in either arm and were censored. (G) Volumes of 1° contralateral untreated tumors in the R-LM113 and R-115 arms, and in naïve mice, at d 20 and 27 after its implantation. Statistical significance was calculated by means of the t-test. The number of mice in the naïve, R-LM113 and R-115 arms were 15, 4, 8, and 14, 4, 7 at d 20 and 27 after implantation of the contralateral tumor, respectively. The mice decreased in number because of deaths caused by the primary tumor. Four and 6 mice in the R-LM113 and R-115 arms, respectively, survived the primary tumor, received the 1° contralateral tumor and were included in the LS group (Fig 5).