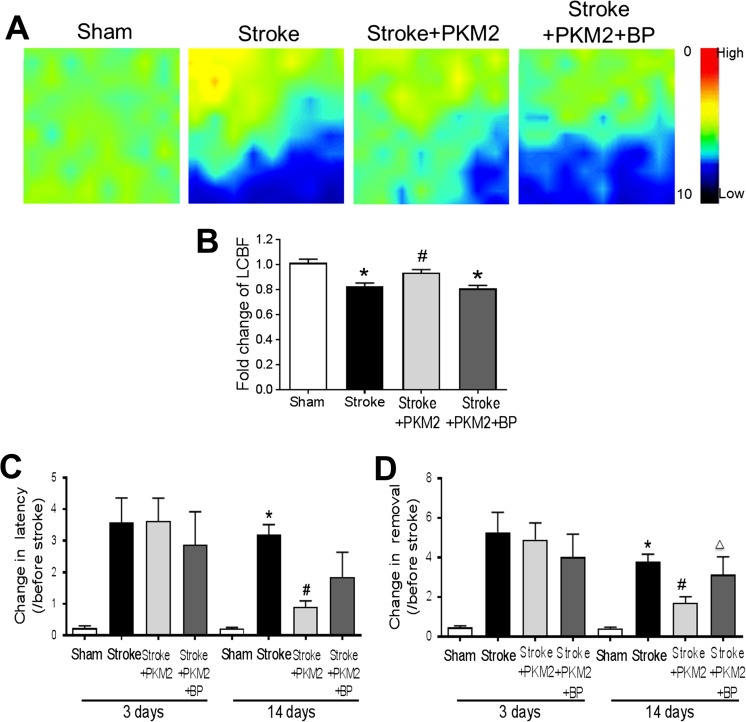
Fig. 7.
rPKM2 improved LCBF restoration and attenuated the behavioral deficits after ischemic stroke. A The local cerebral blood flow (LCBF) in the peri-infarct region was measured 14 days after stroke using a laser Doppler image scanner. B The restoration of LCBF in each group was calculated by the ratio of the mean value of LCBF to the value before stroke. rPKM2 treatment promoted the LCBF restoration and STAT3 inhibitor BP-1-102 abolished the effect of rPKM2. Asterisk, p < 0.05 versus sham; number sign, p < 0.05 versus stroke; delta, p < 0.05 versus stroke + PKM2. n = 7 in sham group, n = 13 in stroke group, n = 7 in stroke + PKM2 group, and n = 8 in stroke + PKM2 + BP (BP-1-102) group. C and D Adhesive removal test was used to assess sensorimotor function 3 and 14 days after stroke. The time needed for stroke animals to feel (time to contact) and remove the sticky dot from the left paw (time to remove) was recorded. The ischemic insult resulted in prolonged time for the stroke animals to remove the sticky dot 3 and 14 days after stroke. Fourteen days after stroke, animals that received rPKM2 treatment showed a significantly shorter time in feeling the sticky dot on their left paws, compared with stroke animals that received either vehicle control or a combination of rPKM2 and BP-1-102. 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni test. Asterisk, p < 0.05 versus sham; number sign, p < 0.05 versus stroke; delta, p < 0.05 versus stroke + rPKM2. n = 5 in sham group; n = 8 in stroke group, stroke + PKM2 group, and stroke + PKM2 + BP (BP-1-102) group