Figure 6.
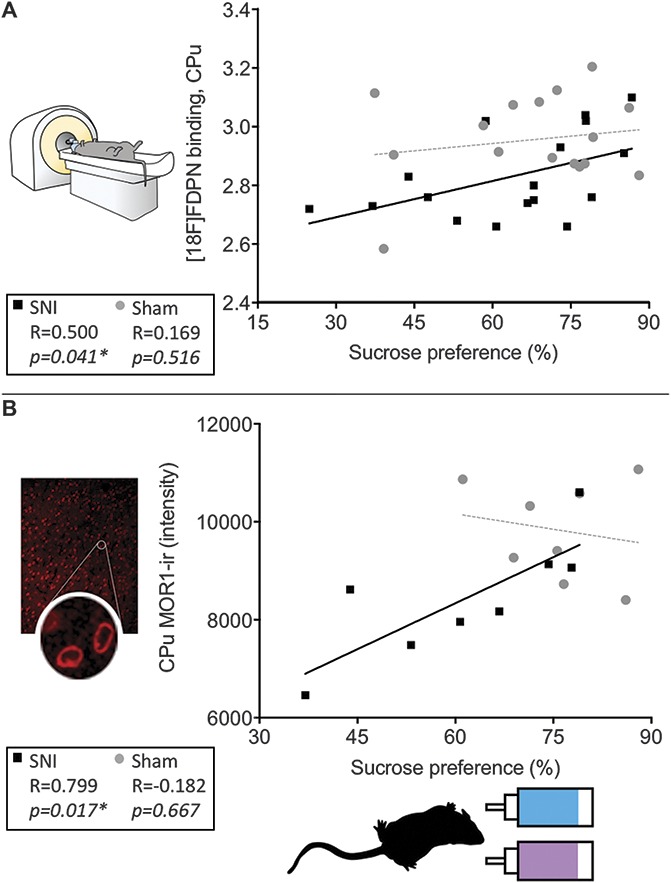
Postinjury sucrose hedonics positively associated with [18F]-FDPN binding and MOR1 expression in the Cpu. (A) Sucrose preference scores of the nerve-injured rats at 3 months after surgery were positively correlated with opioid receptor availability in the caudate–putamen (R = 0.500, P = 0.041, n = 17) as well as with (B) MOR1-ir intensity in the caudate–putamen (R = 0.799, P = 0.017, n = 8). Sucrose preference for the sham group was not significantly correlated with either (A) opioid receptor availability (R = 0.169, P = 0.516) or (B) MOR1-ir intensity (R = 0.182, P = 0.667). P < 0.05 was considered significant in all cases. *P < 0.05. SNI, spared nerve injury.
