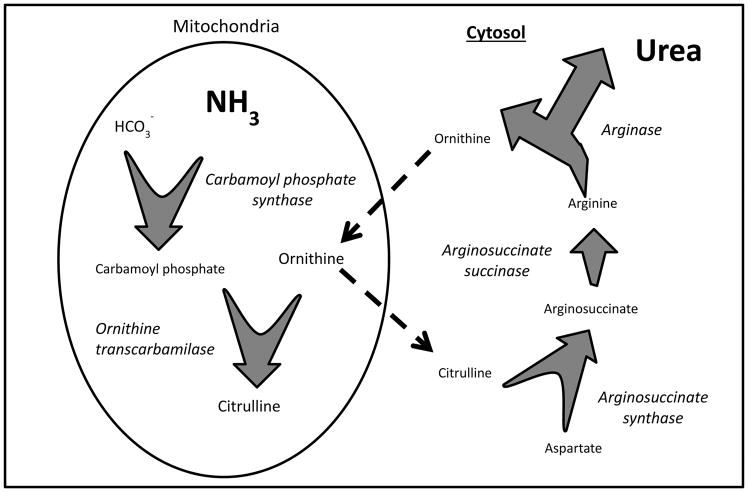
Figure 1. Urea cycle.
Within the mitochondria, an ATP-dependent reaction of bicarbonate and ammonia is catalyzed by carbamoyl phosphate synthase, which is the rate limiting step of the cycle. Carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine form citrulline in a reaction catalyzed by ornithine transcarbamylase. Citrulline enters the cytosol and, using further ATP, is metabolized to arginosuccinate, and in turn to arginine. The hydrolysis od arginine by arginase completes the urea cycle by releasing a urea molecule, and the ornithine re-enters the mitochondria.