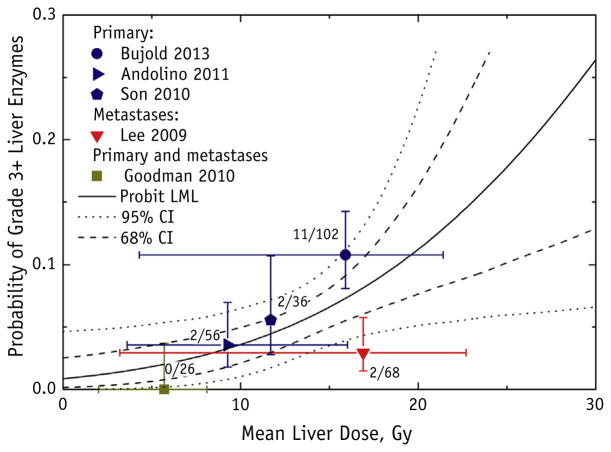
Fig. 1.
Grade ≥3 liver enzyme toxicity as a function of mean liver dose (MLD), with probit model fit and 95% and 68% confidence intervals (CIs). Dose “error bars” (horizontal axis) for each data point represent range of reported doses for each study; toxicity “error bars” (vertical axis) represent binomial 68% CIs. The number of patients who developed toxicity of the total number of patients for each study is displayed next to the data point. All studies excluded the gross tumor volume in the MLD calculation, with the exception of Son et al (20). Probit model fitting failed to establish the upper confidence limit for the dose to 50% of the target, and the null hypothesis of no dose response was not rejected (P = .10); therefore, we could not exclude that the incidence of liver enzyme complications was independent of the dose; the probit model fit is displayed for reference. Abbreviation: LML = log maximum likelihood.