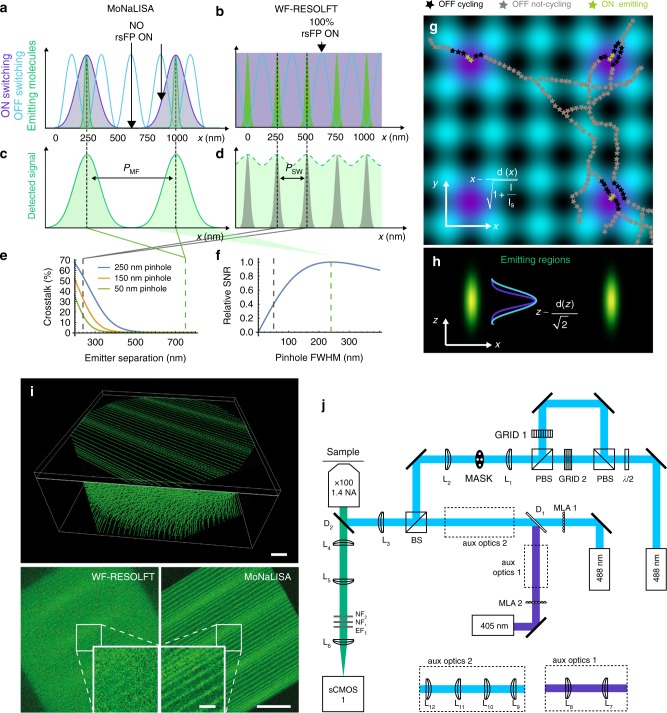
Fig. 1.
Basic concept and imaging scheme. 1D representation of MoNaLISA (a) and wide-field RESOLFT (b) illuminations. The ON-switching (violet) and the excitation are multiple Gaussian foci (periodicity PMF) in MoNaLISA and homogenous in WF-RESOLFT. The OFF-switching light (blue, periodicity PSW) confines the fluorescence emission (green). Detected fluorescence distributions for MoNaLISA (c) and WF-RESOLFT (d) as green area. e The larger foci separation PMF > PSW in MoNaLISA allows detection of the whole fluorescence signal without crosstalk. f Fluorescence collection efficiency for different sizes of digital pinholing. MoNaLISA 250 nm optimal size (green dashed line) increases photon collection and SNR compared to the 50 nm pinholing of WF-RESOLFT (gray dashed line). g 2D calculation of the MoNaLISA illumination: ON-switching and excitation (violet), OFF-switching (blue). Filaments showing rsFPs in different states are illustrated. MoNaLISA minimizes ON–OFF cycling since most of rsFP facing OFF light maxima are in the OFF state. Scale bars, 250 nm. h The fluorescence confinement is extended in 3D as shown in the x–z section. Scale bars, 250 nm. i Simulations show that the combination of increased photon collection, saving rsFP switching cycles and 3D confinement of MoNaLISA images allow imaging of structures which are not observed in WF-RESOLFT. The simulated structure is composed of straight lines with varying separation (~80–300 nm) in planes separated by 300 nm along the optical axis. Scale bars, 1 μm (top), 2.5 μm (large bottom), and 500 nm (zoom inset). j Schematic representation of the optical set-up. MLA 1, MLA 2: microlens arrays, GRID 1, GRID 2: diffraction gratings, PBS polarizing beam splitter, BS non-polarizing beam splitter with 90/10 or 50/50 reflection/transmission, MASK custom-built mask to let through only the orders 1 and −1 of the two orthogonally polarized beams, NF notch filter, EF emission filter, and D dichroic mirror. L1: f = 100 mm, L2: f = 300 mm, L3: f = 300 mm, L4: f = 250 mm, L5: f = 250 mm, L6: f = 200 mm, L7: f = 200 mm. Aux optics 1. L9: f = 200 mm, L10: f = 150 mm, L11: f = 250 mm, L12: f = 250 mm. Aux optics 2. L7: f = 100 mm, L8: f = 100 mm