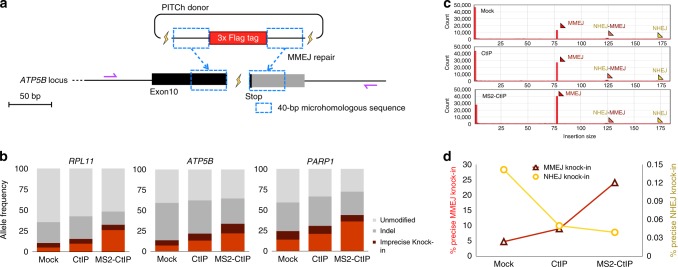
Fig. 2.
High dependence on MMEJ in the enhanced PITCh knock-in. a Schematic of PITCh knock-in of a short tag for NGS analysis. An ~50-bp 3× Flag tag sequence was knocked-in, and then all the amplified products using the primers illustrated by purple arrows were analyzed. This schematic only shows gene targeting in the ATP5B locus, but other gene loci such as PARP1 and RPL11 were targeted in a similar way. b Summary of the frequency of the alleles detected by NGS analysis. Precise knock-in includes MMEJ-dependent knock-in alleles without mutations. For the details of data analysis, see Methods available in the online version of this paper. c Histograms of the read counts at the ATP5B locus, separated by the lengths of inserts. MMEJ, MMEJ/NHEJ, and NHEJ show the expected sizes of the inserts mediated by MMEJ at both knock-in junctions, NHEJ at one junction and MMEJ at the other, and NHEJ at both junctions, respectively, as illustrated in Supplementary Figure 11a. Similar results were obtained at the other two loci (Supplementary Fig. 11c). d Percentages of precise knock-in alleles mediated by MMEJ and NHEJ among total NGS reads at the RPL11 locus. Similar results were obtained at the other two loci (Supplementary Fig. 12b)