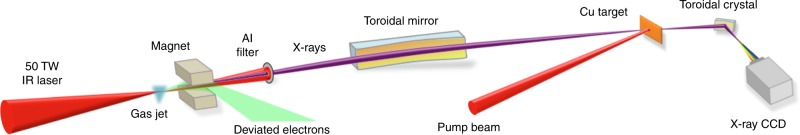
Fig. 2.
Setup of the experiment. A 50 TW, 30 fs laser pulse is focused onto a supersonic jet of 99% helium/1% nitrogen gas mixture. The interaction of the laser with the underdense created plasma yields the generation of a betatron X-ray pulse (see Methods for details). The latter is focused by a toroidal mirror on the Cu sample placed at normal incidence. A spectrometer composed of a toroidal crystal and an X-ray charge-coupled device (CCD) camera then record the transmitted spectrum. In parallel, a synchronized laser pulse (pump), with adjustable delay with respect to the X-ray pulse and with adjustable fluence, is used to heat the Cu sample up to the WDM regime. The absence of jitter is ensured by the fact that the pump laser and the laser-generated X-ray pulse originate from the same laser source