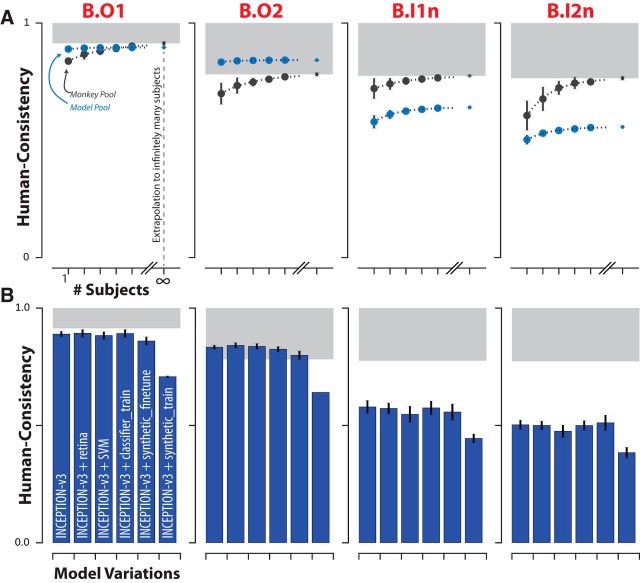
Figure 4.
Effect of subject pool size and DCNN model modifications on consistency with human behavior. A, For each of the four behavioral metrics, the human consistency distributions of monkey (blue markers) and model (black markers) pools are shown as a function of the number of subjects in the pool (mean ± SD, over subjects). Human consistency increases with growing number of subjects for all visual systems across all behavioral metrics. The dashed lines correspond to fitted exponential functions and the parameter estimate (mean ± SE) of the asymptotic value, corresponding to the estimated human consistency of a pool of infinitely many subjects, is shown at the right most point on each abscissa. B, Model modifications that aim to rescue the DCNNIC models. We tested several simple modifications (see Materials and Methods) to the most human consistent DCNNIC visual system model (Inception-v3). Each panel shows the resulting human consistency per modified model (mean ± SD. over different model instances, varying in random filter initializations) for each of the four behavioral metrics.