Fig. 4.
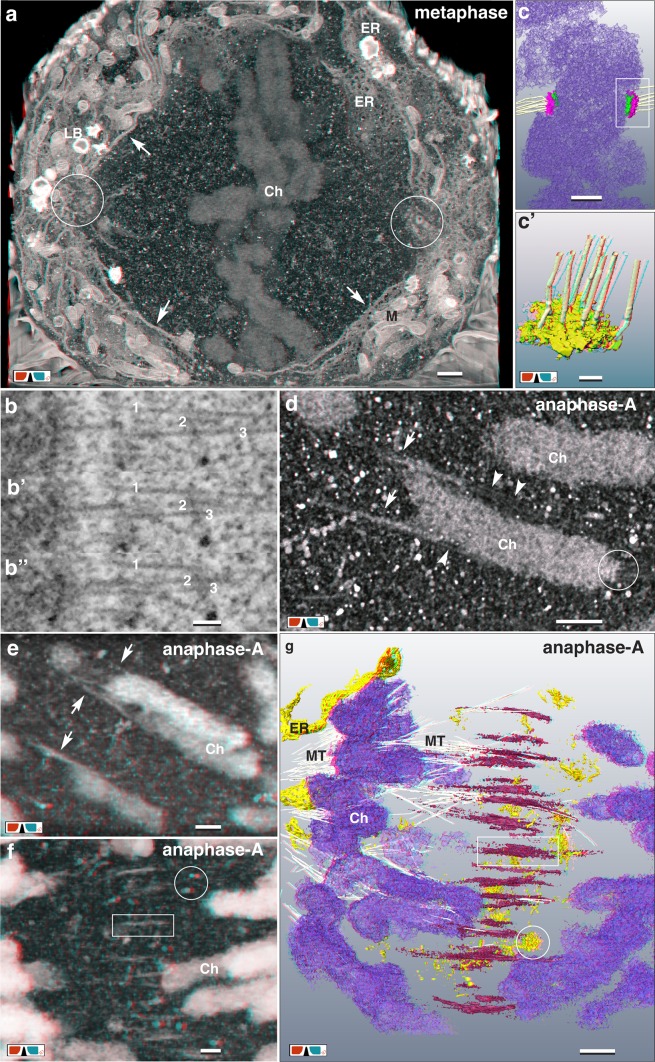
From meta- to anaphase: kinetochores and midzone formation. a Chromosomes (Ch) of a metaphase plate surrounded by a fenestrated ER-cage (arrows). Several layers of ER-sheets at the spindle poles are in contact to the centrosomes (circles), probably acting as an anchor. Scale bar 1 µm. b, b’, b’’ Due to an ablation rate of only 6 nm/section, single MTs, attached to the kinetochore are visible on several consecutive FIB/SEM micrographs. Scale bar 100 nm. c, c’ 3D-reconstruction of sister kinetochores with their disc-like structure of the larger outer kinetochore (pink) and the smaller inner kinetochore (green). 6–7 MT are attached to the kinetochore. c’ = detail of c. Scale bar in c 500 nm; in c’ 100 nm. d Anaglyph image of microtubules (arrowheads) passing the chromosomes flanks, acting as central spindle MTs. Electron dense strands (arrows) seem to be pulled out from the ends of the chromosomes by MTs. Circle marks the kinetochore. Scale bar 500 nm. e Anaglyph image of strands of chromatin (arrows), in contact to MTs, emanate laterally from the chromosome arms in anaphase-A. Scale bar 500 nm. f Anaglyph image (volume rendering at low resolution for high depth information) of clamp-like structures are arranged midway between the dividing chromosomes (rectangle) in anaphase-A. Characteristic for the midzone is the presence of numerous, electron dense single or aggregated vesicular–tubular clusters (circle). Scale bar 500 nm. g Anaglyph image of 3D-reconstruction of chromosomes and midzone in anaphase-A. Clamps (red) are up to 2 µm long and bundle MTs (for clarity only a few are labeled). Halfway between the separating chromosomes (purple), they are arranged in a plane. Numerous vesicular-tubular clusters (circle) are located within the midzone. Scale bar 1 µm