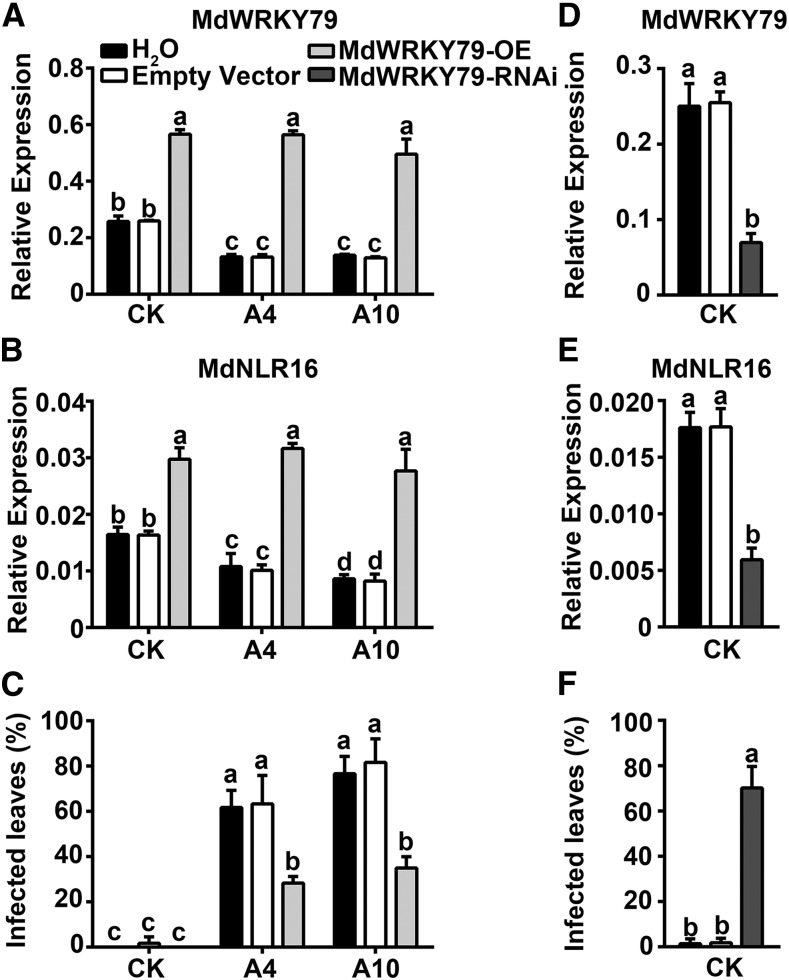
Figure 9.
Overexpression of MdWRKY79 in A4 and A10 Leaves Enhances Resistance, Whereas RNAi Suppression of MdWRKY79 Expression in Wild-Type Control Leaves Decreases Resistance to A. alternata R2.
Infiltration of Agrobacterium solution containing pGWB551-MdWRKY79 (overexpression) or pGWRNAi-WRKY79 vector and subsequent inoculation of A. alternata R2 were performed as in Figure 4, with water and empty vector as controls.
(A) and (B) Transcript levels of MdWRKY79 and MdNLR16 in response to overexpression of MdWRKY79 detected via quantitative RT-PCR, respectively, just before the R2 inoculation.
(C) Percentage of infected leaves three days after inoculation with R2 following overexpression of MdWRKY79 in the wild-type CK and antisense lines A4 and A10.
(D) and (E) Transcript levels of MdWRKY79 and MdNLR16 in wild-type control CK in response to RNAi suppression of MdWRKY79 detected via RT-qPCR just before R2 inoculation, respectively.
(F) Percentage of infected leaves after RNAi suppression of MdWRKY79 expression. Data are mean ± sd of three biological replicates with 10 leaves pooled from five in vitro shoots per replicate for RT-qPCR or 40 leaves pooled from 20 in vitro shoots per replicate for disease evaluation. Different letters (a to d) indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between treatments across genotypes using Duncan’s MRT after ANOVA.