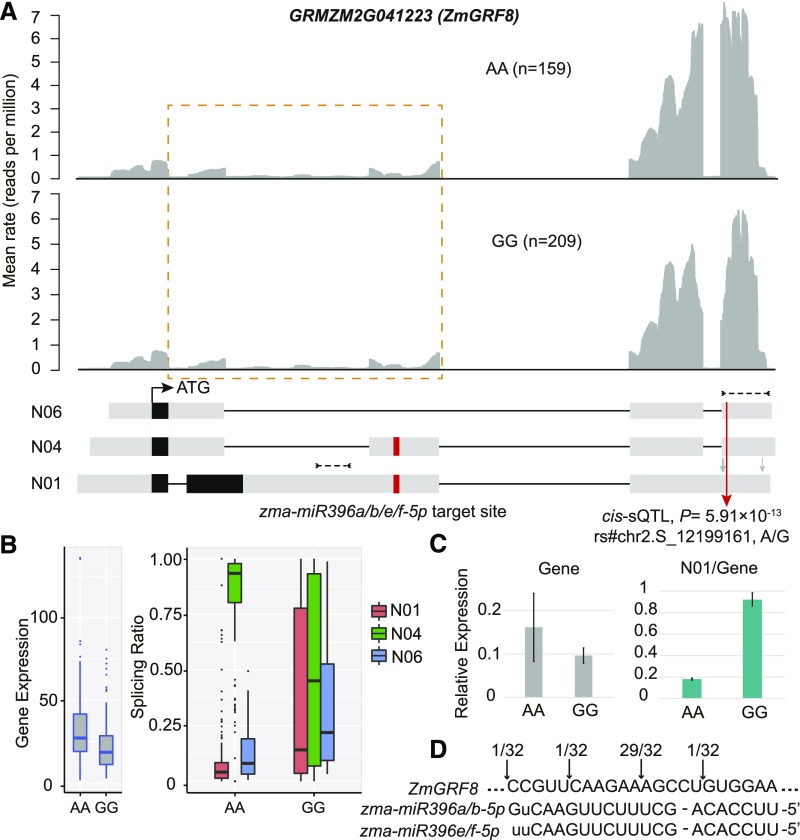
Figure 7.
AS-Coupled miRNA Regulation.
(A) An example of the AS-coupled miRNA mechanism. GRMZM2G041223 was detected with a significant cis-sQTL. For the transcript model, UTRs are shown in gray boxes on the two sides, and CDSs are shown in black boxes in the middle. Lines indicate introns. Transcripts named “N” stand for newly assembled transcript. Red arrow indicates the position of cis-sQTL SNP, and gray arrows indicate the position of other less significant SNPs. The positions of primers used for RT-qPCR are indicated by dotted lines with arrows. For the upper panel, the average rate at each base on the gene is plotted, where individuals were stratified according to their genotype (AA and GG) at sQTL SNP rs#chr2.S_12199161. Brown dotted box shows where transcript structures differ. Red box indicates the position of miRNA target site.
(B) Significant changes in splicing ratio and overall gene expression level at sQTL SNP rs#chr2.S_12199161.
(C) RT-qPCR results. For each genotype at the sQTL, four inbred lines were randomly selected from the maize association panel for the RT-qPCR assay of kernels at 15 DAP. Values represent the mean ± sd of the measurements (n = 4).
(D) RLM-5′-RACE mapping of ZmGRF8 mRNA cleavage sites. The numbers of clones with particular termini are indicated by arrows.