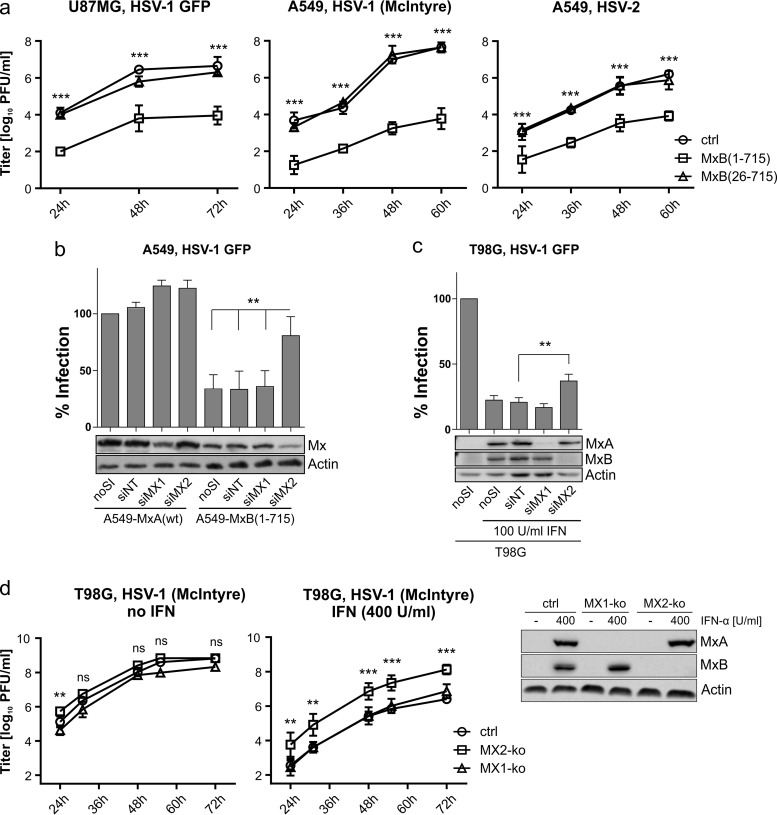
FIG 2.
Herpesvirus infectivity is restricted at multiple time points and can partially be rescued by MxB depletion. (a) Growth kinetics (MOI of 0.0001) of HSV-1 GFP (17+) on U87MG cells and HSV-1 (McIntyre) and HSV-2 (MS) on A549 cells. The titers determined by plaque assay are shown as arithmetic means ± standard deviations (SD) of results from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed on log values of the titers via two-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey's test. P values were determined by comparing the mean titers of control (ctrl) and MxB(1-715) cells at the depicted time points. (b) MxB- or MxA-expressing A549 cells were treated with siRNA as indicated and subsequently infected with HSV-1 GFP (MOI of 0.5) for 20 h. Infectivity was analyzed as described for Fig. 1. Error bars represent the SEM of results from three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed via one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey's test. (c) Nontreated or IFN-α-pretreated T98G cells (100 U/ml for 16 h) were treated and analyzed as described for panel b. (d) T98G cells with specific MX1 and MX2 gene knockouts were left untreated or pretreated with IFN-α (400 U/ml for 16 h) and then infected with HSV-1 strain McIntyre (MOI of 0.001). IFN-α treatment was continued during the whole experiment. Virus titers in the supernatants of the cultures were determined at the indicated time points by plaque assay. The expression of MX1 and MX2 in the different cell lines was detected by Western blotting using MxA- and MxB-specific antibodies. The titers determined by plaque assay are shown as arithmetic means ± SD of results from three independent experiments. Significance is depicted for the MX2 knockout (MX2-ko) strain relative to the control cells and was determined via two-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey's test. ***, <0.001; **, <0.01; ns, nonsignificant.