FIG 1.
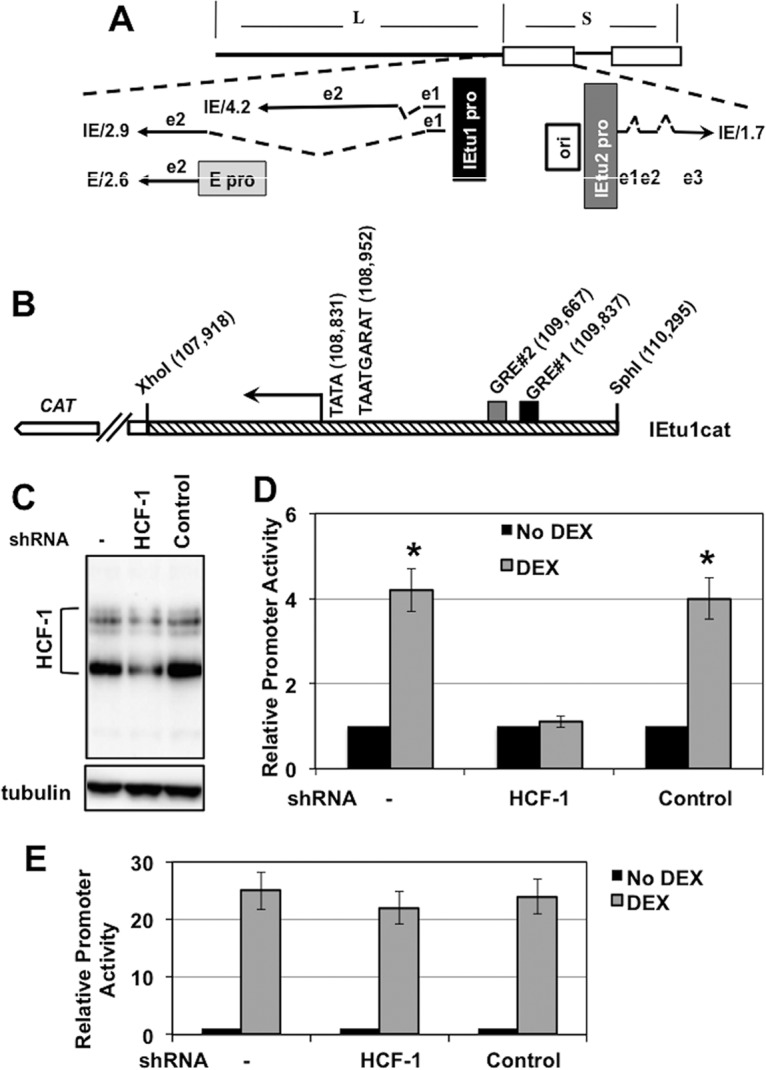
Regulation of IEtu1 promoter activity by DEX. (A) Location of IE transcripts and promoters that drive their expression during productive infection (23–25). IE/4.2 encodes the bICP4 protein, and IE/2.9 encodes the bICP0 protein. One IE promoter activates expression of IE/4.2 and IE/2.9 (IEtu1, black rectangle). A second bICP0 transcript (E/2.6) is expressed from an early promoter (E pro; gray rectangle). The IEtu2 promoter (IEtu2 pro) drives expression of the bICP22 protein. Solid lines in the transcript position map represent exons (e1, e2, or e3), and dashed lines denote introns. ORI, origin of replication. (B) Schematic of the IEtu1 promoter (IEtu1cat) with the transcription initiation site (arrow), TATA box, TAATGARAT core, and GRE sites (GRE#1 and GRE#2). The genomic coordinates of the first nucleotide of each respective motif are shown. (C) Neuro-2A cells were mock transfected (−) or transfected with plasmids that express an HCF1-specific shRNA or a control shRNA. At 24 h posttransfection, resolved cell lysates were probed for HCF-1 and control tubulin. (D) Neuro-2A cells were transfected with plasmids that express an HCF1-specific shRNA (shRNAc504) or a control shRNA. Twenty-four hours later, cells were cotransfected with the IEtu1 promoter-reporter and a plasmid expressing the mouse GR and subsequently treated with vehicle or 10 μM water-soluble DEX. Reporter activity is shown in the presence or absence of DEX treatment. The results are averages ± standard deviations (SD) from 3 independent experiments, and the asterisk denotes a significant difference relative to other samples (P < 0.05 by Student t test). (E) Neuro-2A cells were mock transfected (−) or cotransfected with the indicated plasmids expressing the HCF-1 shRNA (c504) or control shRNA. Twenty-four hours later, cells were transfected with an MMTV LTR reporter. The reporter activity is shown in the presence or absence of DEX treatment. The results are averages ± SD from 3 independent experiments.
