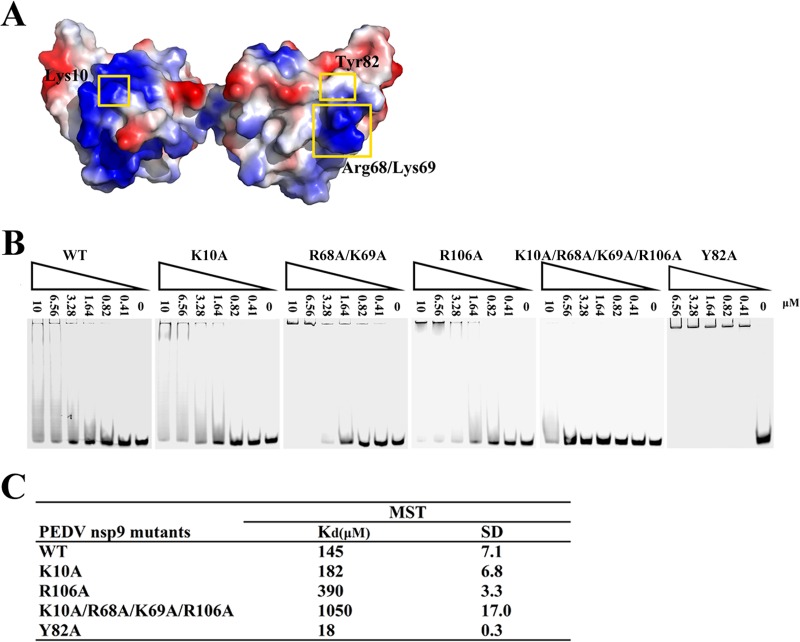
FIG 7.
Impact of positively charged amino acid substitutions on ssDNA binding of PEDV nsp9. (A) Depictions of the electrostatic potential surface of the PEDV nsp9 dimer created by APBS tools. The mutated amino acids exposed on the protein surface are labeled. (B) The ssDNA binding abilities of nsp9-WT, nsp9-K10A, nsp9-R68A, K69A, nsp9-R106A, nsp9-K10A/R68A/K69A/R106A, and nsp9-Y82A as determined by EMSA. Each protein was assayed at different concentrations (0, 0.41, 0.82, 1.64, 3.28, 6.56, and 10 μM) with 5 μM 5′-Cy5-labeled 36-mer ssDNA. (C) The ssDNA binding affinities of nsp9-WT, nsp9-K10A, nsp9-R106A, nsp9-K10A/R68A/K69A/R106A, and nsp9-Y82A as measured by MST assays. Each protein was used in 2-fold concentration steps with 10 nM 5′-Cy5-labeled 36-mer ssDNA. The measured Kd of each protein is shown in the table.