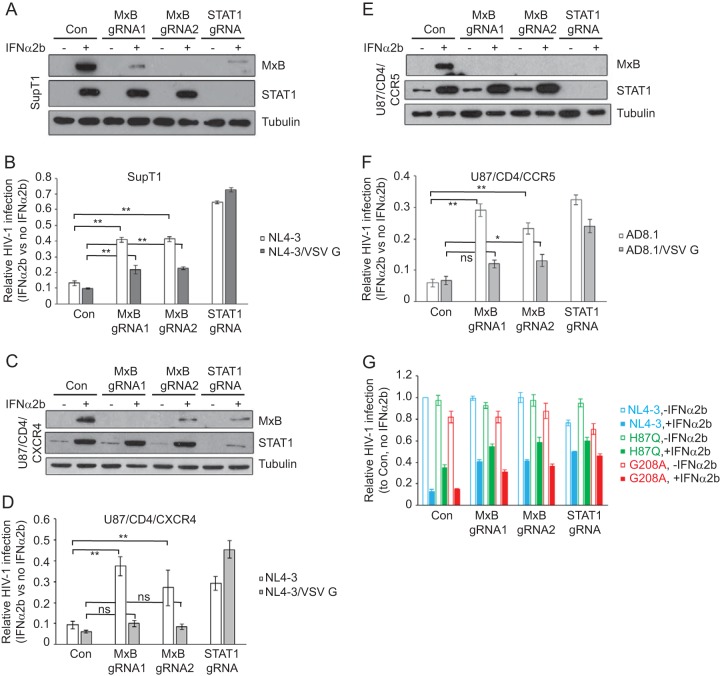
FIG 2.
Depletion of MxB in SupT1 and U87/CD4 cells rescues HIV-1 infection under IFN-α2b treatment. (A) Levels of MxB and STAT1 in the control SupT1 cells and in SupT1 cells that were stably transduced with Cas9/gRNA in the absence and presence of IFN-α2b (500 U/ml). The levels of tubulin served as the internal control. (B) IFN-α2b (500 U/ml) suppression of HIV-1 infection, without or with VSV G protein pseudotyping, in the control and knockout SupT1 cells. Relative HIV-1 infection was calculated with the values in the absence IFN-α2b arbitrarily set as 1. (C) Levels of MxB and STAT1 in control and knockout U87/CD4/CXCR4 cells in the absence and presence of IFN-α2b. (D) IFN-α2b (100 U/ml) suppression of HIV-1 NL4-3 or VSV-G-pseudotyped NL4-3 (NL4-3/VSV G) in control and knockout U87/CD4/CXCR4 cells. (E) Results of Western blotting to show the depletion of MxB and STAT1 in U87/CD4/CCR5 cell lines that were stably transduced with Cas9/gRNA. (F) IFN-α2b (100 U/ml) suppression of HIV-1 AD8-1 or VSV-G-pseudotyped AD8-1 (AD8-1/VSV G) in the control and MxB knockout U87/CD4/CCR5 cell lines. The results shown are the averages from three independent infections of the knockout cell lines. (G) IFN-α2b (500 U/ml) suppression of HIV-1 H87Q and G208A mutants in the control SupT1 cells or in SupT1 cells with MxB or STAT1 knockout. The level of wild-type HIV-1 NL4-3 infection in the control SupT1 cells in the absence of IFN-α2b was arbitrarily set as 1. The infection levels of the H87Q and G208A mutants were calculated accordingly. The results shown are the averages from three independent infection experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ns, not significant.