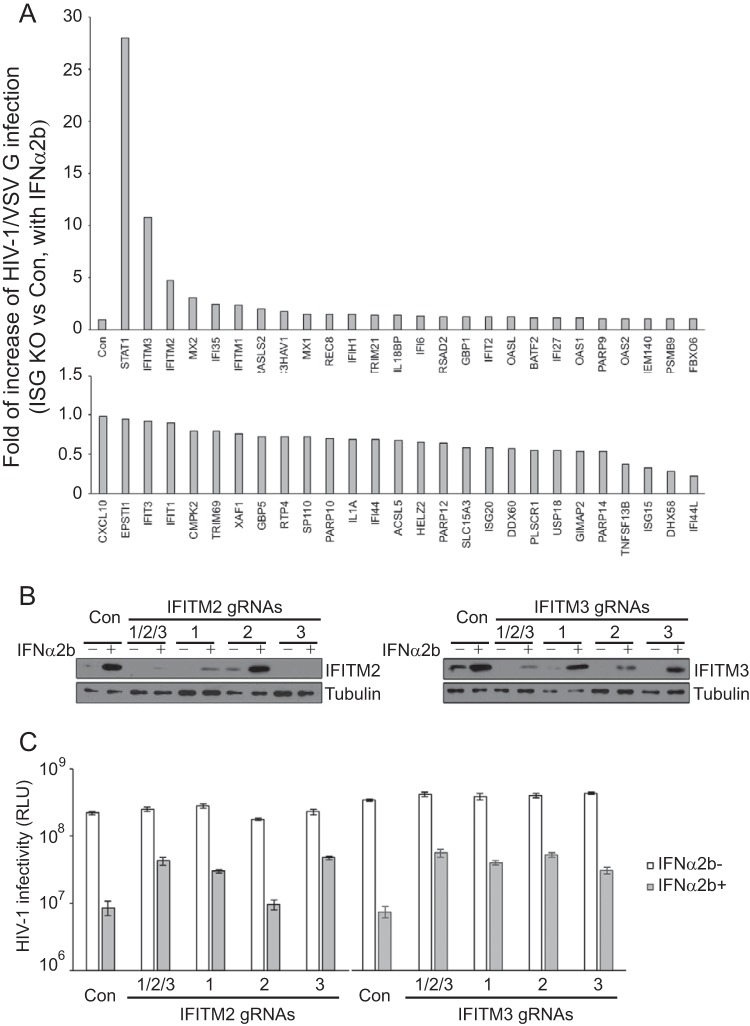
FIG 6.
Cas9/gRNA knockout screen in U87-MG cells for ISGs that alleviate IFN-α2b inhibition of HIV-1 NL4-3/VSV G. (A) Effects of ISG knockout (KO) on IFN-α2b (100 U/ml) suppression of HIV-1 NL4-3/VSV G infection. Fifty-three ISGs were selected for the knockout study. For each ISG, a pool of three gRNAs was used to stably transduce U87-MG cells. NL4-3/VSV G infection was monitored by measuring the levels of viruses produced through infection of TZM-bl cells. IFN-α2b suppression of NL4-3/VSV G infection was calculated by dividing the amount of viruses produced in the presence of IFN-α2b by the amount of viruses produced without IFN-α2b treatment. The value from control cells in each screening experiment is arbitrarily set as 1, so that all the data from multiple experiments can be summarized in the bar graph. If the value from an ISG knockout cell line is greater than 1, then the knockout of this ISG leads to an increase in HIV-1/VSV G infection in the presence of IFN-α2b. The results shown are the averages from two independent screens of all 53 ISGs. For clarity, data are presented in two graphs. (B) Results of Western blotting to show the levels of IFITM2 or IFITM3 in the U87-MG knockout cell lines. Three gRNAs were tested for IFITM2 or IFITM3. One cell line was created using all three gRNAs (1/2/3) to achieve maximal knockout efficiency. (C) IFN-α2b (100 U/ml) inhibition of NL4-3/VSV G infection in IFITM2 or IFITM3 knockout U87-MG cell lines. The levels of viruses that were produced in the absence or presence of IFN-α2b were determined by infecting TZM-bl indicator cells. The results shown are the averages from three independent infections. RLU, relative luciferase units. Error bars indicate standard deviations.