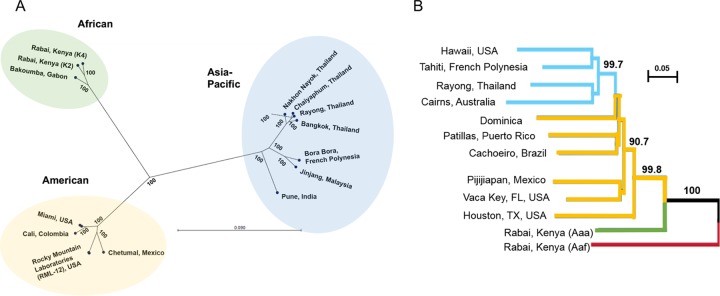
FIG 5.
AeAV strains have evolved into African, Asia-Pacific, and American lineages. (A) Maximum likelihood phylogeny (PhyML) between AeAV strains using a GTR + G + T model with 1,000 bootstraps. Branch lengths represent expected numbers of substitutions per nucleotide site. For visual clarity, the RML-12 clade and Miami clades were collapsed and single examples are shown. (B) Evolutionary history of worldwide sampling of A. aegypti, adapted from references 60 and 61, from 1,504 SNP species. Bootstrapped neighbor-joining network based on population pairwise chord distances with node support over 90% is shown on relevant branches. New World (American) populations are in yellow, and Asia-Pacific populations are shown in light blue. We have truncated the tree and rooted it to A. aegypti formosus (Aef), shown as a red branch.