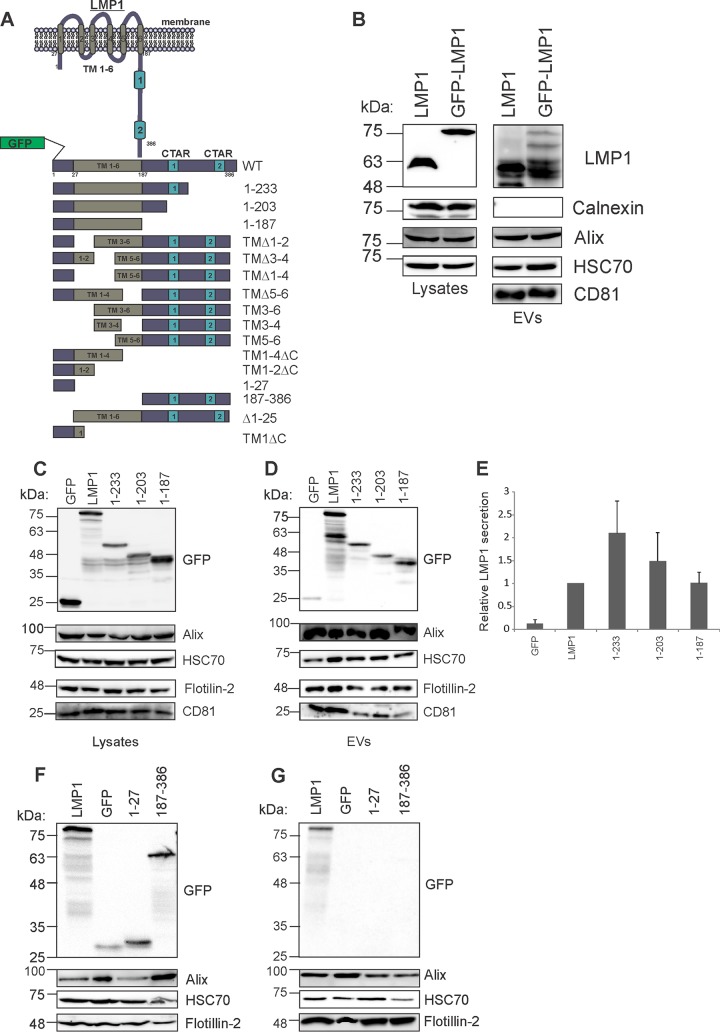
FIG 1.
The C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of LMP1 is not required for EV packaging. (A) Schematic depiction of WT GFP-tagged LMP1 and deletion mutants. LMP1 is a six-pass transmembrane protein with N- and C-terminal cytoplasmic tails. Various GFP-tagged mutants of the full-length wild-type LMP1 protein were constructed by PCR mutagenesis and used throughout the study. (B) The levels of nontagged LMP1 and GFP-LMP1 were compared in cell lysates and EVs. (C) Lysate immunoblot analysis of cells transiently transfected with LMP1 or mutants containing deletions in the C terminus (1-233, 1-203, and 1-187) (equal protein masses were loaded). (D) EVs (equal volumes were loaded) were harvested by differential centrifugation and analyzed by immunoblot analysis for GFP-tagged proteins and common EV markers (Alix, HSC70, Flotillin-2, and CD81). (E) Semiquantitative immunoblot analysis of the results of 3 independent experiments. The levels of LMP1 mutant secretion are relative to wild-type LMP1 secretion and normalized to cellular expression and EV production [(LMP1EV/HSC70EV)/(LMP1cell/HSC70cell)]. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (F) Cell lysates and (G) EVs harvested from GFP, GFP-LMP1, or GFP-tagged N (1-27) and C (187-386) termini of LMP1. Cells and EVs were harvested by differential centrifugation and analyzed by immunoblotting for expression with anti-GFP antibody and common EV markers (Alix, HSC70, and Flotillin-2). TM, transmembrane domains.