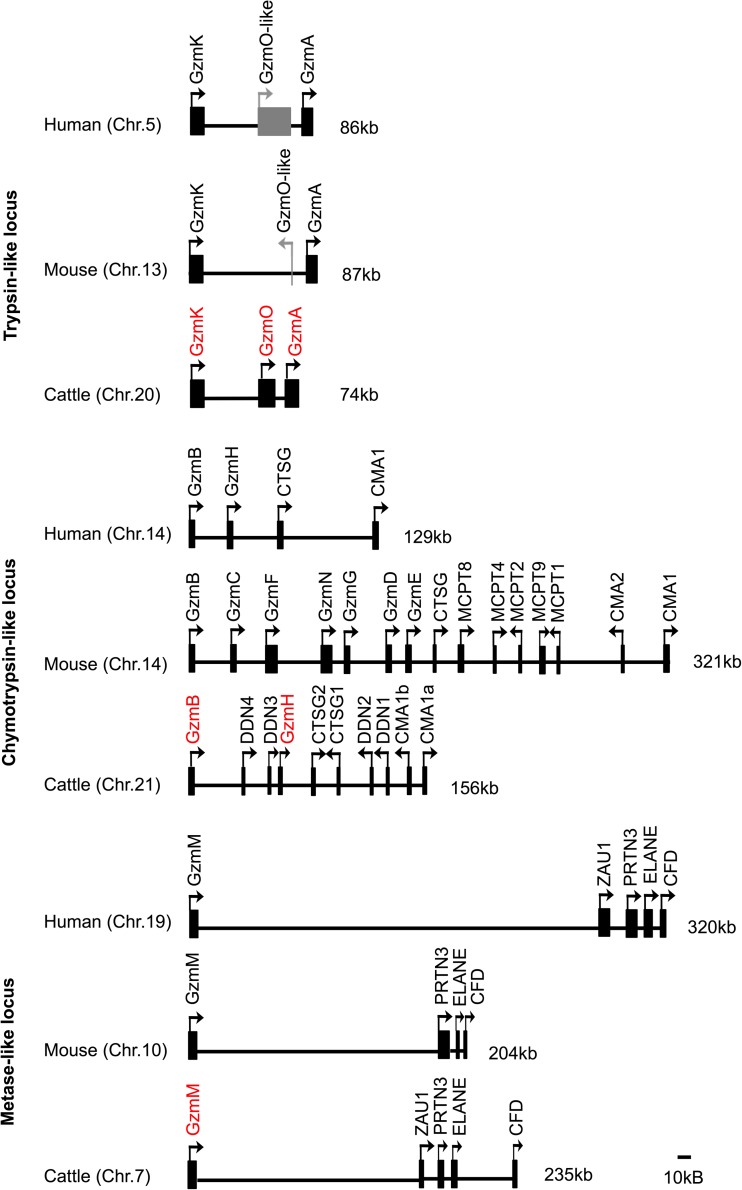
Fig. 2.
Comparison of the genomic organisation of the human, murine and cattle granzyme loci. Human and murine loci were drawn based on the genome assembly of GRCh38.p12 and GRCm38.p6, respectively. Three corresponding loci of trypsin-like (chr 20: 24,033,747–24,107,687), chymotrypsin-like (chr 21: 35,112,322–35,267,979) and metase-like (chr 7: 44,797,942–45,032,845) were drawn based on bovine genome assembly (UMD3.1 (GCA_000003055.3). Bars indicate gene positions; arrows indicate transcriptional orientation; numbers on the right-hand side of loci indicate the length of locus. Intervals between genes are drawn to scale. Bovine granzyme genes are highlighted in red. Functional genes are shown in black boxes and non-functional genes in grey. Chr = chromosome; Gzm = granzyme; CTSG = cathepsin G; CMA = mast cell a-chymase; DDN = duodenase; ZAU1 = azurocidin 1; PRTN3 = proteinase 3; ELANE = neutrophil elastase preproprotein; CFD = complement factor D