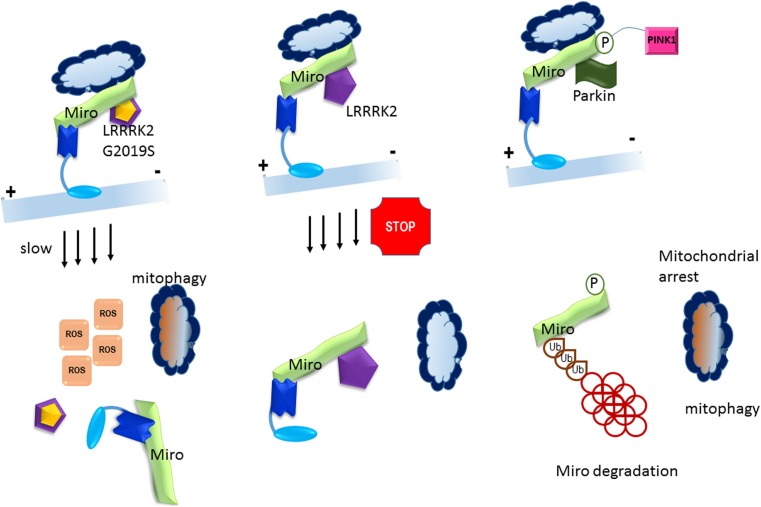
Fig. 3.
Miro in Parkinson’s disease. A = LRRK2, promotes Miro removal by forming a complex with Miro. Pathogenic mutant LRRK2G2019S disrupts this function, delaying the arrest of damaged mitochondria and consequently slowing the initiation of mitophagy. Mitochondrial motility and Miro degradation are shown to be impaired in PD patients. Direct interaction of LRRK2 with Miro results in Miro removal from mitochondria. In pathogenic LRRK2 mutant G2019S this is deranged delaying the arrest of damaged mitochondria and consequently slowing the initiation of mitophagy. Knockdown in Miro levels in LRRK2G2019S human neuron and Drosophila PD models rescued neurodegeneration. Miro degradation and mitochondrial motility are also impaired in sporadic PD patients. B = Parkinson’s disease implicated PINK1 kinase and Parkin play an important role in quality control of mitochondrial survival and apoptosis through Miro GTPase. Dysfunctional mitochondria are destroyed after PINK1 accumulation that phosphorylated Miro at S156 and also Parkin to activate its E3 ligase activity. This results in proteosomal degradation of Miro and mitochondrial arrest and mitophagy