Figure 2.
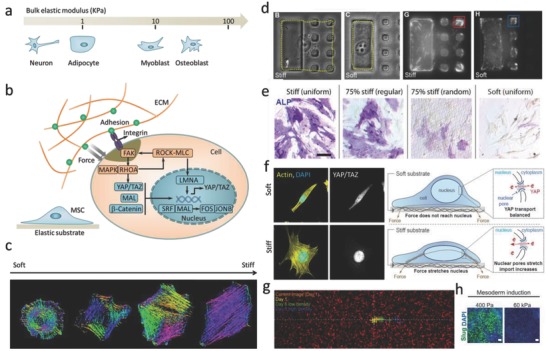
Bulk stiffness regulates stem cell fate. a) The differentiation of MSCs toward particular lineages is regulated by substrates with stiffness that is similar to native tissues. b) Mechanotransduction pathways inside cells regulate cell fates. c) Actin cytoskeleton organization depends on substrate stiffness. The different colors indicate different orientations of actin filaments. Reproduced with permission.9 Copyright 2015, Nature Publishing Group. d) A micropatterned platform that limits cells to a stiff region stimulates durotaxis. Reproduced with permission.10 Copyright 2014, National Academy of Sciences (United States). e) Spatially patterned matrix elasticity directs stem cell differentiation. Reproduced with permission.11 Copyright 2016, National Academy of Sciences (United States). f) Stiffness triggers nuclear YAP localization by regulating transport across nuclear pores. Reproduced with permission.12 Copyright 2017, Cell Press. g) Stiffness gradient affects cell migration, cells can migrate from soft to stiff. Reproduced with permission.13 Copyright 2017, National Academy of Sciences (United States). h) Stiffness determines embryonic stem cell differentiation. Reproduced with permission.14 Copyright 2016, Cell Press.
