Figure 5.
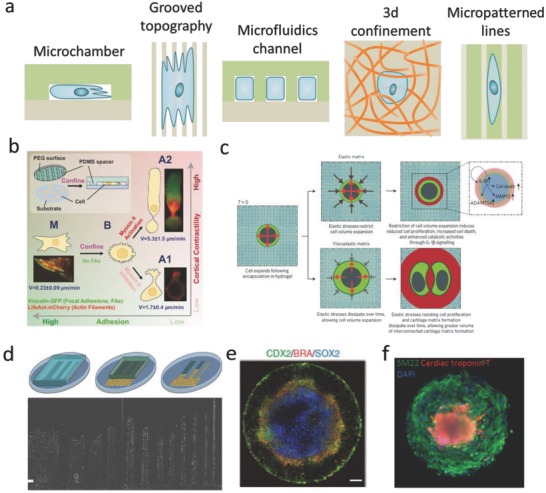
The effect of confinement on cell behavior. a) Schematics of engineered models of confining microenvironments. b) Cells migrate fast in confined environments because of low adhesion. Reproduced with permission.46 Copyright 2015, Cell Press. c) Mechanical confinement regulates cartilage matrix formation by chondrocytes. Reproduced with permission.47 Copyright 2017, Nature Publishing Group. d) Confinement affects cell migration. Reproduced with permission.[[qv: 22a]] Copyright 2012, National Academy of Sciences (United States). e) Confinement environment is sufficient to induce patterned differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Reproduced with permission.48 Copyright 2014, Nature Publishing Group. f) Geometric confinement induced self‐organizing human cardiac microchambers. Reproduced with permission.49 Copyright 2015, Nature Publishing Group.
