Figure 9.
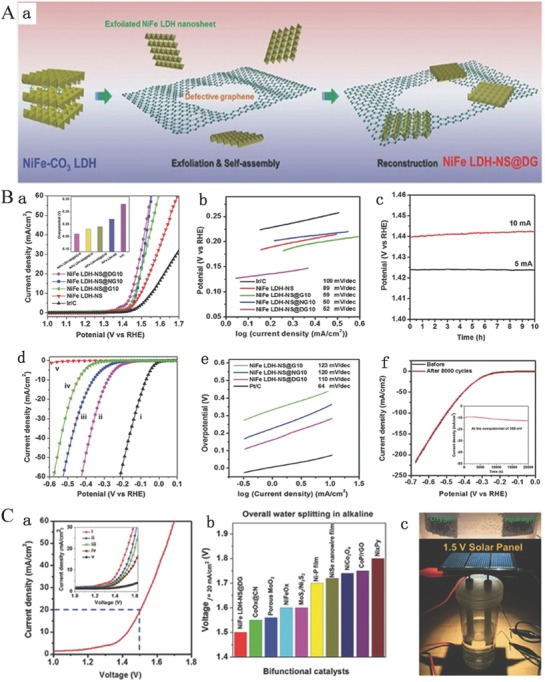
A) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of NiFe LDH‐NS@DG nanocomposite a). B) Electrochemical performance of all synthesized electrocatalysts for OER and HER. a) The LSV curves of all synthesized electrocatalysts for OER in 1 m KOH electrolyte. Inset: The overpotential required at 10 mA cm−2. b) The corresponding Tafel slopes for OER. c) Chronopotentiometry curves of the NiFe LDH‐NS@DG10 at constant current densities of 5 and 10 mA cm−2, respectively. d) The LSV curves of all synthesized electrocatalysts for HER in 1 m KOH electrolyte. e) The corresponding Tafel slopes for HER. d) The LSV curves for the NiFe LDH‐NS@DG10 before and after 8000 CV cycles. C) The curve of overall water splitting for NiFe LDH‐NS@DG10 on nickel foam with a loading of 2 mg cm−2 as bifunctional catalyst in 1 m KOH a). b) To achieve 20 mA cm−2, the required voltage for the NiFe LDH‐NS@DG catalyst and other non‐noble metal bifunctional catalysts. c) Demonstration of a solar power–assisted water‐splitting device with a voltage of 1.5 V. Reproduced with permission.158 Copyright 2017, Wiley‐VCH.
