Figure 10.
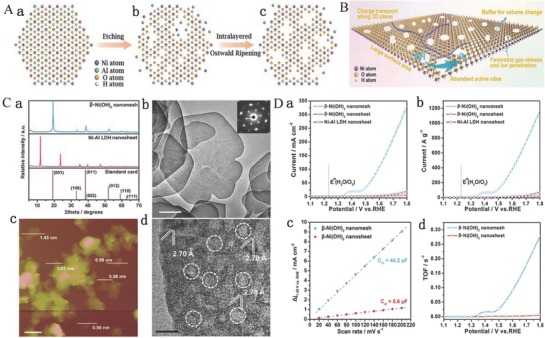
A) The synthesis model of single‐crystalline β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes. a) The structure of a Ni–Al LDH monolayer. b) The porous β‐Ni(OH)2 nanosheets with various pore sizes after etching by strong alkaline solution. c) The formation of single‐crystalline β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes with abundant and uniform nanopores by the interlayered Ostwald ripening process. B) The structural benefits of the β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes as OER electrocatalyst. C) Characterization. a) XRD patterns of the single‐crystalline β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes and as‐exfoliated Ni–Al LDH nanosheets; TEM b), AFM c), and HERTEM d) images of the single‐crystalline β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes. D) Electrochemical performances of synthesized catalysts in 1 m KOH electrolyte. a) LSV curves of the single‐crystalline β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes, β‐Ni(OH)2 nanosheets, and as‐exfoliated Ni–Al LDH nanosheets. b) The corresponding mass activity. c) The estimation of Cdl for β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes and β‐Ni(OH)2 nanosheets. d) TOF plots of β‐Ni(OH)2 ultrathin nanomeshes and β‐Ni(OH)2 nanosheets at applied potentials. Reproduced with permission.93 Copyright 2017, Wiley‐VCH.
