Figure 3.
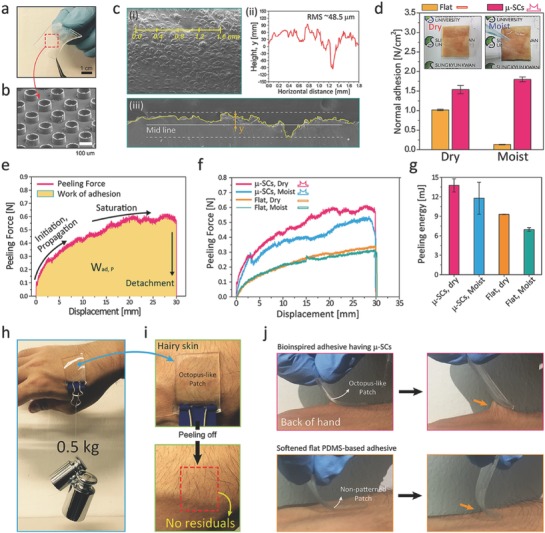
a,b) Photograph a) and SEM b) image of octopus‐like biocompatible PDMS‐based adhesive with enlargeable 3D microtips and μ‐SCs (100 µm in diameter and 75 in µm height: 3 cm × 3 cm and ≈600 µm thickness). c) Morphology analysis of an engaged pigskin with dual‐roughness (see yellow line): top‐view (i), surface‐profile (ii), Cross‐sectional SEM image of macroscale fluctuations (iii). d) Pull‐off strengths for a PDMS‐based μ‐SCs and a nonpatterned PDMS‐patch against a rough pigskin. Here, inset images show dry and moist pigskins. e) Representative displacement‐dependent profile of peeling adhesion on a pigskin. f,g) Peeling adhesion profiles f) and peeling energies g) for two different adhesives (PDMS‐based μ‐SCs and a nonpatterned patch) on dry and moist pigskin. h,i) Demonstration of the bioinspired adhesive (2 × 2 cm2) fully supporting a 0.5 kg weight on hairy skin h) without sticky residuals after detachment i). j) Photographs of an octopus‐inspired adhesive on the hairy skin of a volunteer's hand, indicating higher peel‐strength than a flat, PDMS‐based adhesive. Error bars represent standard deviations (for d and g; N = 10).
