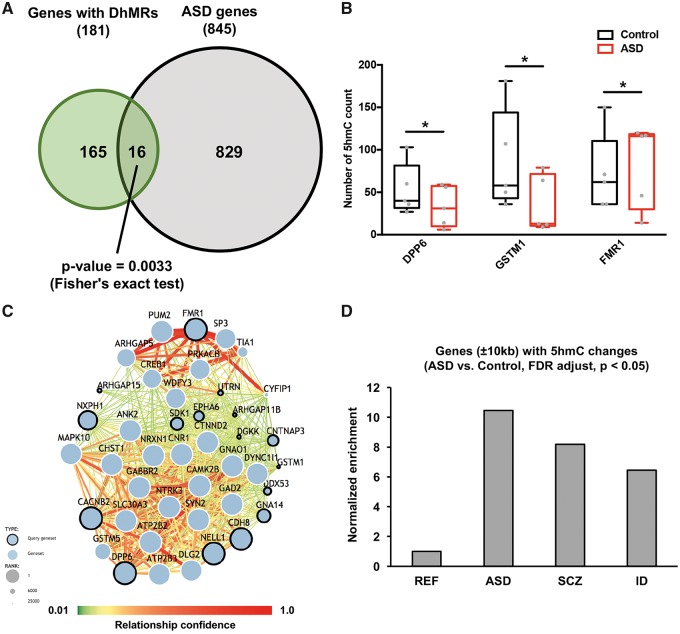
Figure 3.
Bioinformatics analyses reveal the regulatory roles of intragenic DhMRs in ASD. (A) DhMRs-associated genes significantly overlapped with ASD risk genes (P-value = 0.0033, Fisher’s exact test). (B) 5hmC changes in three ASD risk genes, including DPP6, GSTM1 and FRM1, in ASD and control samples (*P < 0.05, FDR adjusted). (C) 5hmC-mediated regulation in ASD candidate genes interactome. Predicted ASD–gene network exploring brain-specific interactions between ASD candidate genes were generated, including 16 DhMRs-associated genes shown with the dots marked with bold lines. (D) 5hmC changes in the ±10 kb region of psychiatric genes, including ASD, SCZ and IDs risk genes. Compared to reference genes; we found a significantly higher fraction of ASD, SCZ and ID risk genes associated with 5hmC changes (P-value = 2.2e-16, Chi-square test).