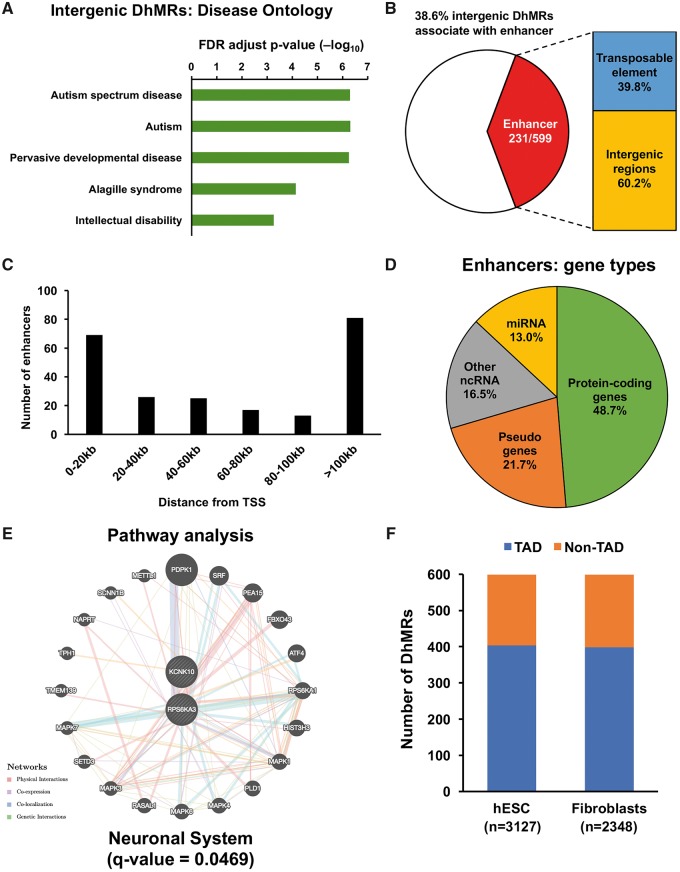
Figure 4.
Predicted cis-regulatory functions of intergenic DhMRs in ASD. (A) Prediction of the cis function of 599 non-coding intergenic DhMRs. A significant association was identified between the intergenic DhMRs and neurodevelopment disorders, particularly ASD and IDs. Intergenic DhMRs overlap with general enhancers in the brain. (B) These identified brain enhancers overlap with 231 out of 599 intergenic DhMRs, 40% of which were located on transposable elements. These DhMRs-associated enhancers were located in different distances from TSS, with the most abundant in 0–20 kb and >100 kb regions (C) and associated with different gene types (D). The pathway and disease association analyses indicated that those protein-coding genes (with enhancers in 100 kb from TSS) were significantly involved in the neuronal system (E). (F) A significant portion of intergenic DhMRs was associated with TADs that were found in hESC (n = 3127) and human IMR90 fibroblasts (n = 2348) cell lines.