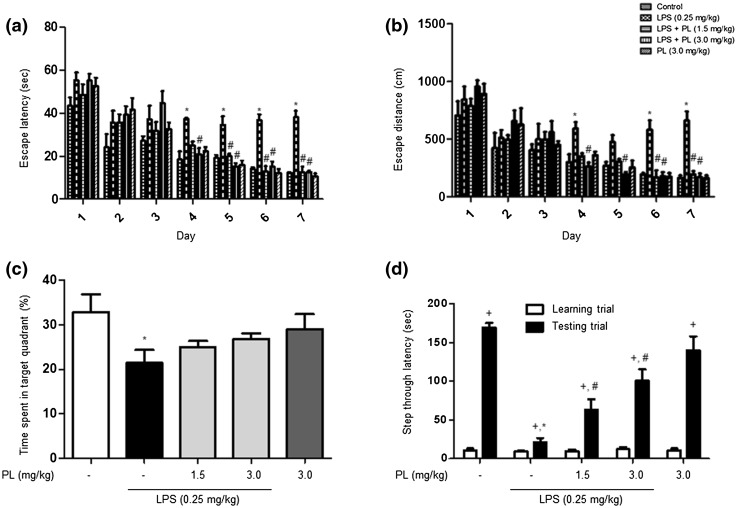
Fig. 2.
Assessments of cognitive functions of mice. Morris water maze were performed two times a day for 7 days. Escape latency (a) and distance (b) to arrive at the platform were automatically recorded. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 7, Two-way ANOVA, *p < .05 vs. control, #p < .05 vs. LPS). After Morris water maze test, a probe test was performed. The time spent in the target quadrant and target site crossing within 60 s (c). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 7, t test, *p < .05 vs. control). Passive avoidance test was performed 1 day after a learning trial test (d). The mice were given an electric shock when they entered into the dark compartment. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 7, t test, +p < .05 vs. each learning trial, *p < .05 vs. control testing trial, #p < .05 vs. LPS testing trial)