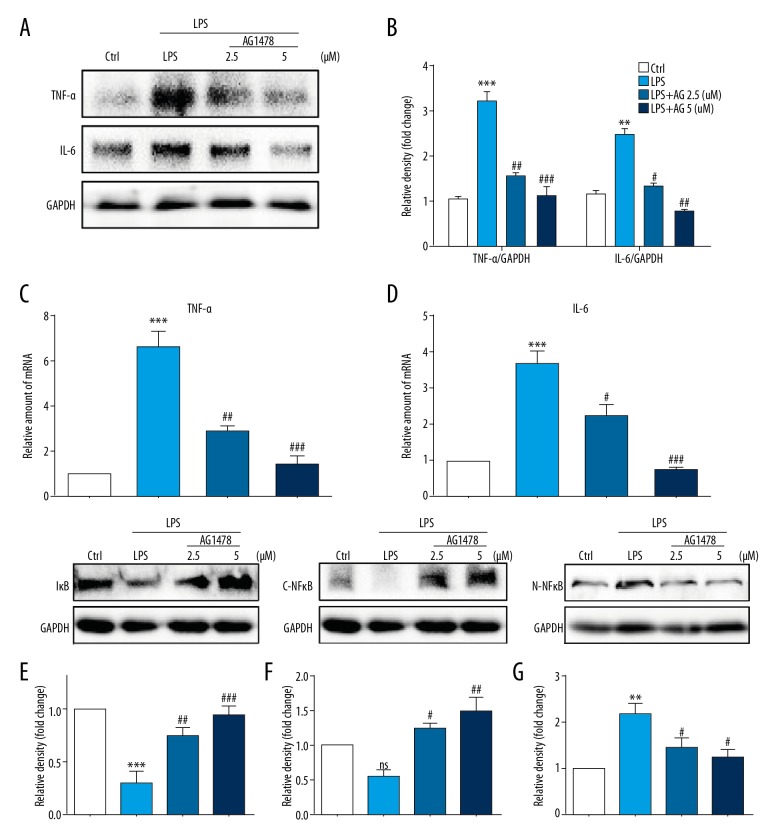
Figure 2.
Treatment with AG1478 reduced levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hepatic stellate cell (HSC) inflammatory cytokines. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were pretreated with AG1478 (2.5 μM and 5 μM) for 2 h, and then exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/mL) for the indicated times. (A, B) HSCs incubated with LPS for 24 h. Levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-6, in the cell lysates were detected by Western blot (A). The figures in the columns show the normalized optical density (OD) for the data from three independent experiments (B). (C, D) HSCs incubated with LPS for 6 h. The mRNA levels of TNF-α (C) and IL-6 (D) were detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and normalized against β-actin. (E–G) Western blot analysis of IκBα (E), cytoplasm NFκB P65 (C-NFκB) (F) and nuclear NFκB P65(N-NFκB) (G) levels in HSCs incubated with LPS for 1h. GAPDH was used as a loading control for IκBα/C-NFκB and laminin B as loading control for N-NFκB. ns – not significant vs. Ctrl group; ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, vs. Ctrl group; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001, vs. the LPS-treated group.