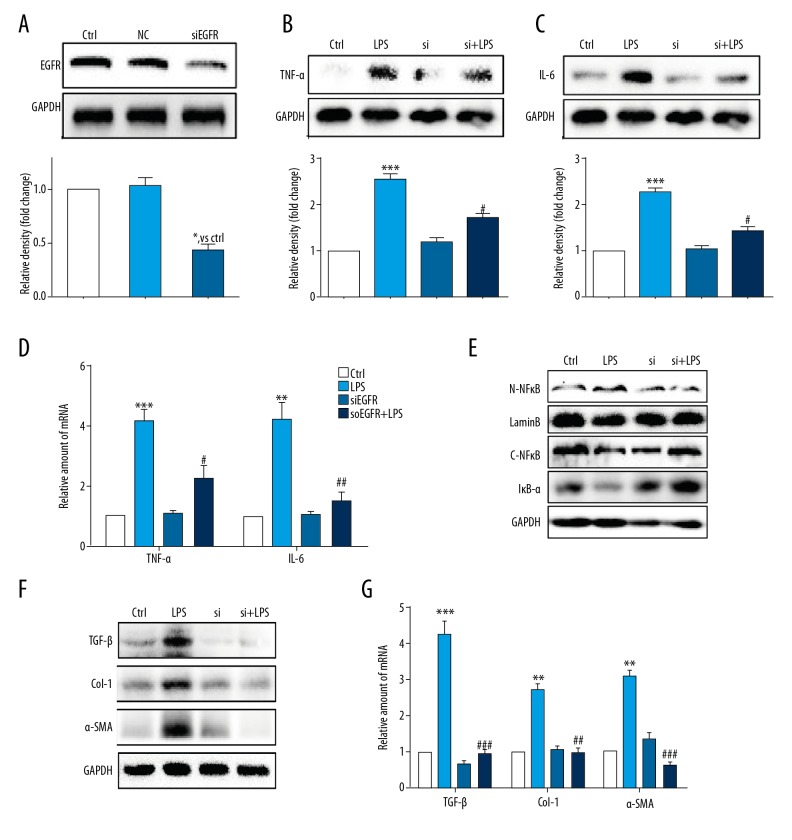
Figure 3.
Knockdown of the EGFR gene following small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced hepatic stellate cell (HSC) injury. (A) Western blot analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) following small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection in HSCs (NC – negative control for transfection). After incubation of the transfected hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) for 24 h, EGFR gene knockdown HSCs were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (100 ng/mL) for the indicated times (Si – EGFR siRNA). (B, C) HSCs incubated with LPS for 24 h. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (B) and interleukin (IL)-6 (C) in cell lysates were detected using Western blot. (D) HSCs incubated with LPS for 6 h. The mRNA levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were detected by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and normalized by β-actin. (E) HSCs incubated with LPS for 1 h. IκB-α, cytoplasm NFκB (C-NFκB), and nuclear NFκB (N-NFκB) protein levels were detected using Western blot. (F) HSCs incubated with LPS for 24 h. The levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, Col-1, and α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) were detected using Western blot. (G) HSCs incubated with LPS for 6 h. The mRNA levels of TGF-β, Col-1, and α-SMA were detected by RT-qPCR and normalized against β-actin. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, vs. Ctrl group; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001, vs. the LPS-treated group.