Figure 1.
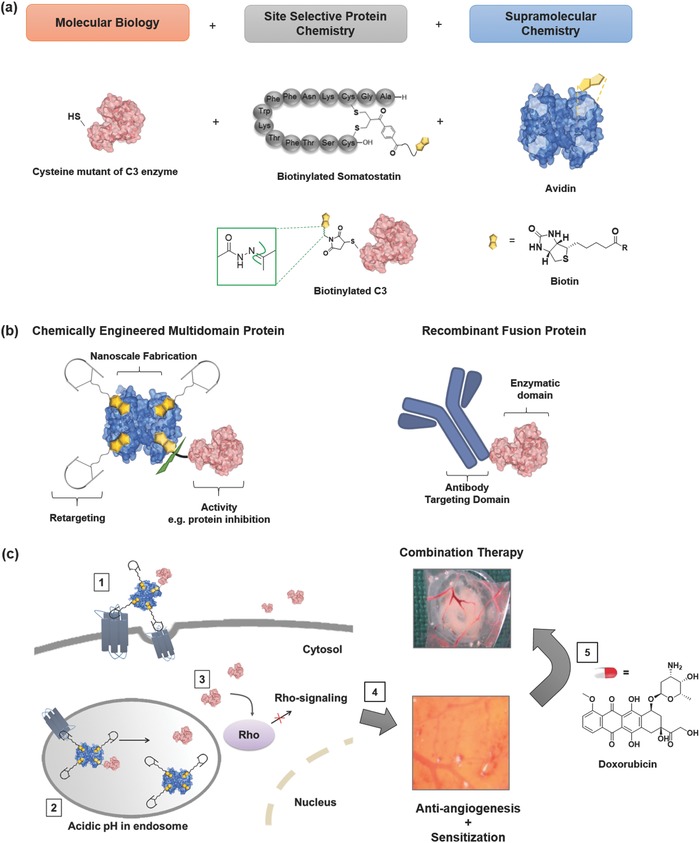
Chemically engineered multidomain protein, SST3‐Avi‐C3, and illustration of the bioactivity of SST3‐Avi‐C3 in tumor inhibition and application in combination with DOX to induce efficient cell death. a) The ensemble of site‐selective chemistry, supramolecular chemistry, and molecular biology is applied to prepare a synthetic multidomain protein complex with desirable features: avidin (blue) is used as the adaptor molecule for chemical fusion of the targeting entity, site‐selectively biotinylated (yellow) somatostatin (SST) to the potent Rho inhibitor (cysteine mutant of the C3 toxin, pink). A hydrazone linkage is introduced site selectively in the design for cleavage at acidic pH (structure in the green inset) to trigger C3 release inside cells. b) A recombinant multidomain antibody enzyme is shown as a comparison of their structural and functional features to the synthetic multidomain protein complex prepared in this study. c) A pictorial representation of the mode of action and synergistic effects of the combination of the chemical fusion toxin and the chemotherapeutic doxorubicin (DOX) in cancer cells: (1) internalization of SST3‐Avi‐C3 into cells via SSTR2‐mediated uptake, (2) cleavage of C3 in the acidic environment of endosomes, (3) release of C3 into the cytosol resulting in Rho inactivation leading to (4) reduced angiogenesis in tumor blood vessels and sensitization of the tumor cells for (5) subsequent co‐administration of conventional anticancer drug, e.g., DOX, finally resulting in efficient cell death at low dosage.
