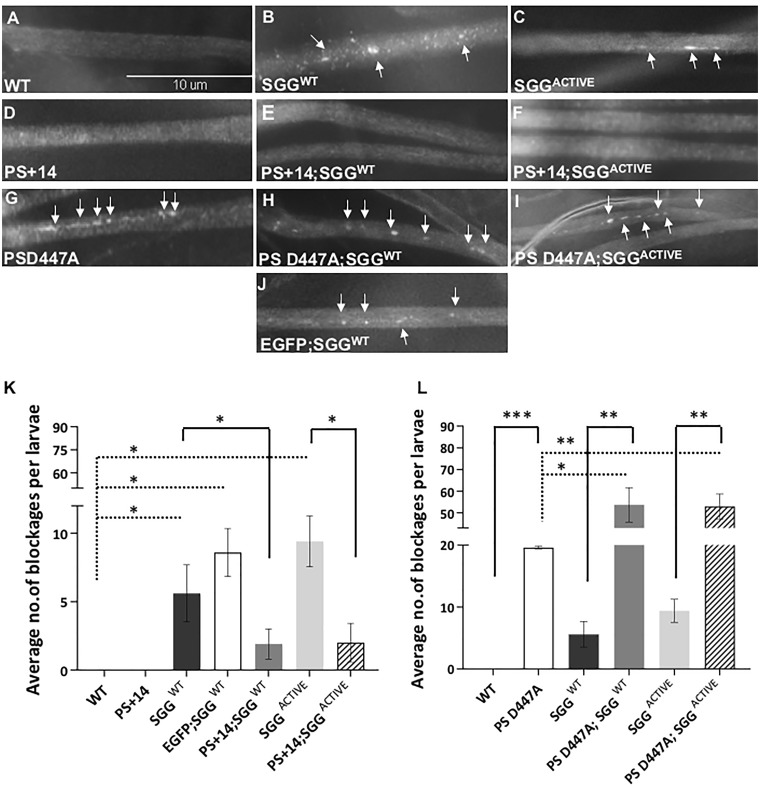
Figure 1.
Expression of functional PS rescues GSK3β-mediated axonal transport defects. (A) A representative larval segmental nerve from WT larva stained with the synaptic vesicle marker Cysteine string protein (CSP) shows smooth staining in their larval nerves. Scale Bar = 10 µm. (B and C) In contrast, larval segmental nerves expressing SGGWT or SGGACTIVE show axonal blockages (arrows) that stain with CSP. (D) Larval segmental nerves from larvae expressing full-length Drosophila PS (PS+14) show smooth CSP stained larval nerves. (E) Larval segmental nerves from larvae expressing PS+14 and SGGWT show smooth CSP staining. (F) Larval segmental nerves from larvae expressing PS+14 and SGGACTIVE also show smooth CSP staining. (G) Larvae expressing a non-functional form of PS, PSD447A show axonal blockages (arrows). (H) Larval segmental nerves from larvae expressing PSD447A and SGGWT show axonal blockages (arrows). (I) Larvae expressing PSD447A and SGGACTIVE also show axonal blockages (arrows). (J) Larvae expressing SGGWT and EGFP show axonal blockages (arrows) similar to larvae expressing SGGWT (B). (K) Quantification analysis shows that the extent of axonal blockages in SGGWT (P = 0.02784), EGFP; SGGWT (P = 0.00538) and SGGACTIVE (P = 0.00721) are significant. The extent of axonal blockages in PS+14.1 and SGGWT or SGGACTIVE is significantly decreased compared with larvae expressing SGGWT (P = 0.04602) or SGGACTIVE (P = 0.01241) alone. N = 5 larvae for each genotype from at least three independent genetic crosses. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, using Student’s t-test). (L) Quantification analysis shows that the extent of axonal blockages in PSD447A is significant (P = 4.48 × 10−5). The extent of axonal blockages in PSD447A; SGGWT or PSD447A; SGGACTIVE larvae compared with PSD447A (P = 0.03108), SGGWT (P = 0.00255) or SGGACTIVE (P = 0.00237) was significant. N = 5 larvae for each genotype from at least three independent genetic crosses. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, using Student’s t-test).