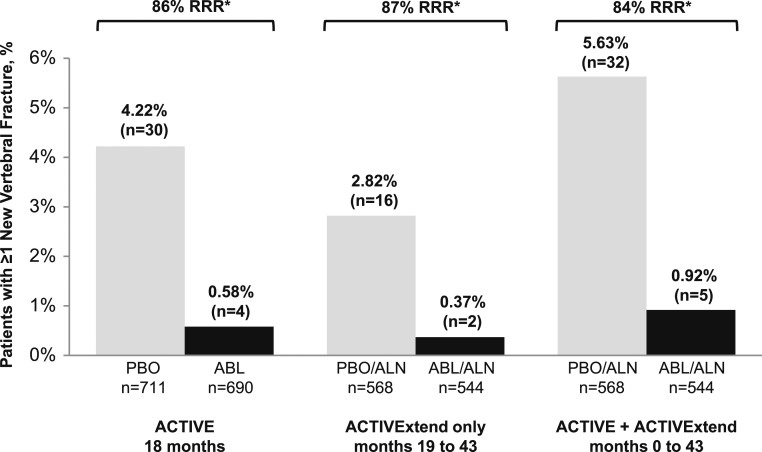
Figure 2.
Incidence of new vertebral fractures in ACTIVE, ACTIVExtend only, and ACTIVE plus ACTIVExtend. mITT populations, representing those participants who had baseline and also postbaseline spinal x-rays at the specified time points, were evaluated for vertebral fracture rates. In ACTIVE, treatment with ABL was associated with an 86% RRR for new vertebral fractures compared with PBO. A gap in treatment of up to 1 mo (from mo 18 to 19) was allowed for rollover and reconsenting from ACTIVE to ACTIVExtend. During the ACTIVExtend period only (mo 19 to 43), prior treatment with ABL was associated with an RRR of 87% compared with prior treatment with PBO. For the full ACTIVE/ACTIVExtend study period (mo 0 to 43), treatment with ABL was associated with an 84% RRR compared with PBO. *P ≤ 0.001 for ABL vs PBO and for ABL/ALN vs PBO/ALN. ACTIVE findings were reported by Miller et al. (9).