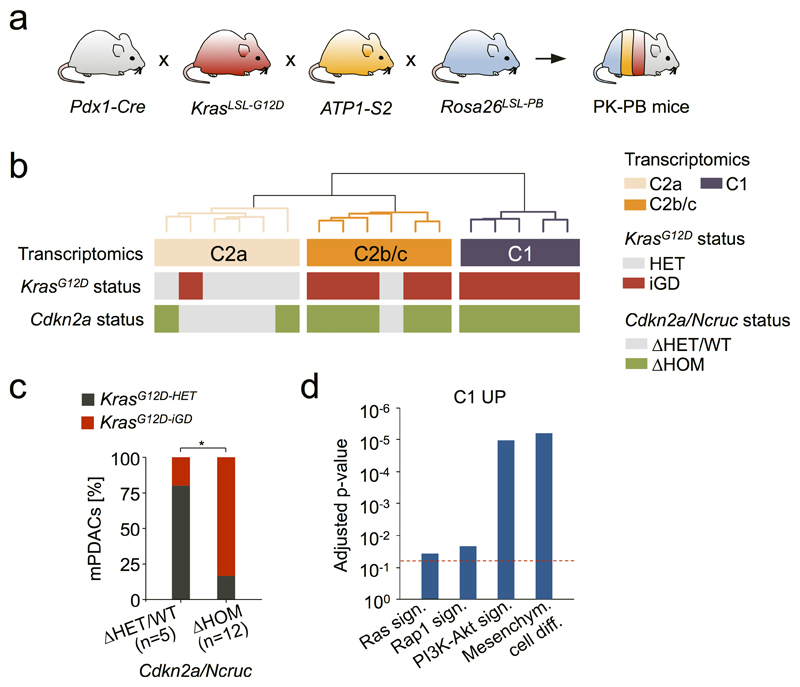
Extended Data Figure 10. KrasG12D-gene dosage is a critical determinant of PDAC biology in a mouse model with high mutational load.
The mutational burden in primary PDAC cultures of PK mice was significantly lower as compared to human PDAC studies (see Fig. 1b). To account for this potential confounding factor and to test if our discoveries in PK mice also apply in a setting of high mutational burden, we used a mouse model combining KrasG12D mutation and PiggyBac transposon-based insertional mutagenesis (PK-PB mice13). PK-PB mice show accelerated tumorigenesis as compared to PK mice. PK-PB derived tumors had an extensive mutational burden (median of 494 transposon insertions per tumor). Primary cultures of PDAC from PK-PB mice (n=17) were subjected to comprehensive genetic characterization using aCGH, microarray-based gene expression profiling, quantitative transposon insertion site sequencing (QiSeq) and amplicon-based deep sequencing of the Kras locus. a, Transcriptome profiles of primary PDAC cultures from PK-PB mice (n=17) were used for unbiased hierarchical clustering that resulted in 2 major clusters (C1 and C2), like in PK mice. KrasG12D gene dosage status (as determined by aCGH and amplicon-based deep sequencing of the Kras locus) and Cdkn2a status (as determined by aCGH and quantitative transposon insertion site sequencing [QiSeq]) are indicated below the cluster tree for each individual tumor. Similarly to PK mice, cluster C2a was characterized by KrasG12D-HET and Cdkn2a/NcrucΔHET/WT status, whereas mPDACs in clusters C2b/c and C1 had increased KrasG12D gene dosage (KrasG12D-iGD) and were Cdkn2a/NcrucΔHOM. The genetic KrasG12D-status was significantly associated with expression clusters (P=0.01, two-sided Fisher’s exact test) providing further evidence that expression clusters are associated with KrasG12D gene dosage. b, Prevalence of KrasG12D-iGD in cultures of primary mPDAC (from PK-PB mice) with homozygous (n=12) or heterozygous/wild-type (n=5) Cdkn2a/Ncruc status. *P=0.03, two-sided Fisher’s exact test, OR 20.0, 95% CI 1.4-287.8. c, Gene set enrichment analysis using DAVID of upregulated genes in cluster C1 (n=5) as compared to cluster C2 (n=12) of primary mPDAC cultures from PK-PB mice. As in PK mice, PK-PB tumors in C1 are characterized by upregulation of genes enriched in gene sets describing mesenchymal cell differentiation and revealed a strong enrichment for Ras downstream signaling pathways (full list in Supplementary Table 19). FDR-adjusted P-values are shown on y axis. Overall, these analyses show that the biological principles discovered in the PK model also apply to pancreatic cancers from PK-PB mice with high mutational load.