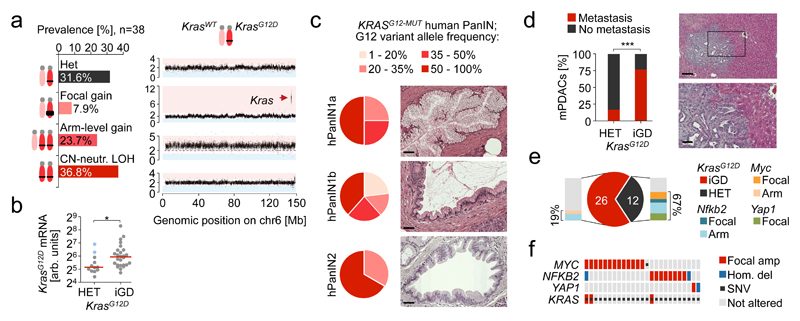
Figure 2. Mutant KRAS gene dosage increase occurs early in PDAC evolution and drives metastasis.
a, KrasG12D gene dosage “states” defined by aCGH, WES and M-FISH (n=38 PK mice). Exemplary CNV-plot for each “state” on the right, y-axis, copy number b, Allele-specific KrasG12D mRNA expression in KrasG12D-iGD (n=26 mice) and KrasG12D-HET mPDACs (n=12 mice) by combined amplicon-based RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR. *P=0.02, two-sided Mann-Whitney test; bars, median. c, Codon-12 variant allele frequency of microdissected KRASG12 mutant hPanIN (n=20) by amplicon-based deep sequencing. H&E stains show histopathologic stages of microdissected hPanINs. Scale bars, 50 µm. d, Macro-/micro-metastasis prevalence in KrasG12D-HET (n=12) vs. KrasG12D-iGD (n=26) mPDACs. (***P=0.001, two-sided Fisher’s exact test). Liver metastasis, H&E. Scale bars, 150 µm (top) and 50 µm (bottom); square, zoom-in area. e, KrasG12D-HET mPDAC amplify alternative oncogenes (Myc, Nfkb2 or Yap1) to intensify partial aspects of Ras downstream signaling. Focal, focal amplification; Arm, arm-level amplification. f, Amplification of MYC, NFKB2 or YAP1 in KRASMUT human PDAC. Note, these amplified genes can not only collaborate with KRASMUT-Het but also with KRASMUT-iGD. Data from6.