Extended Data Figure 4. Enrichment for amplification of alternative oncogenic drivers in mPDACs of PK mice with KrasG12D-HET status.
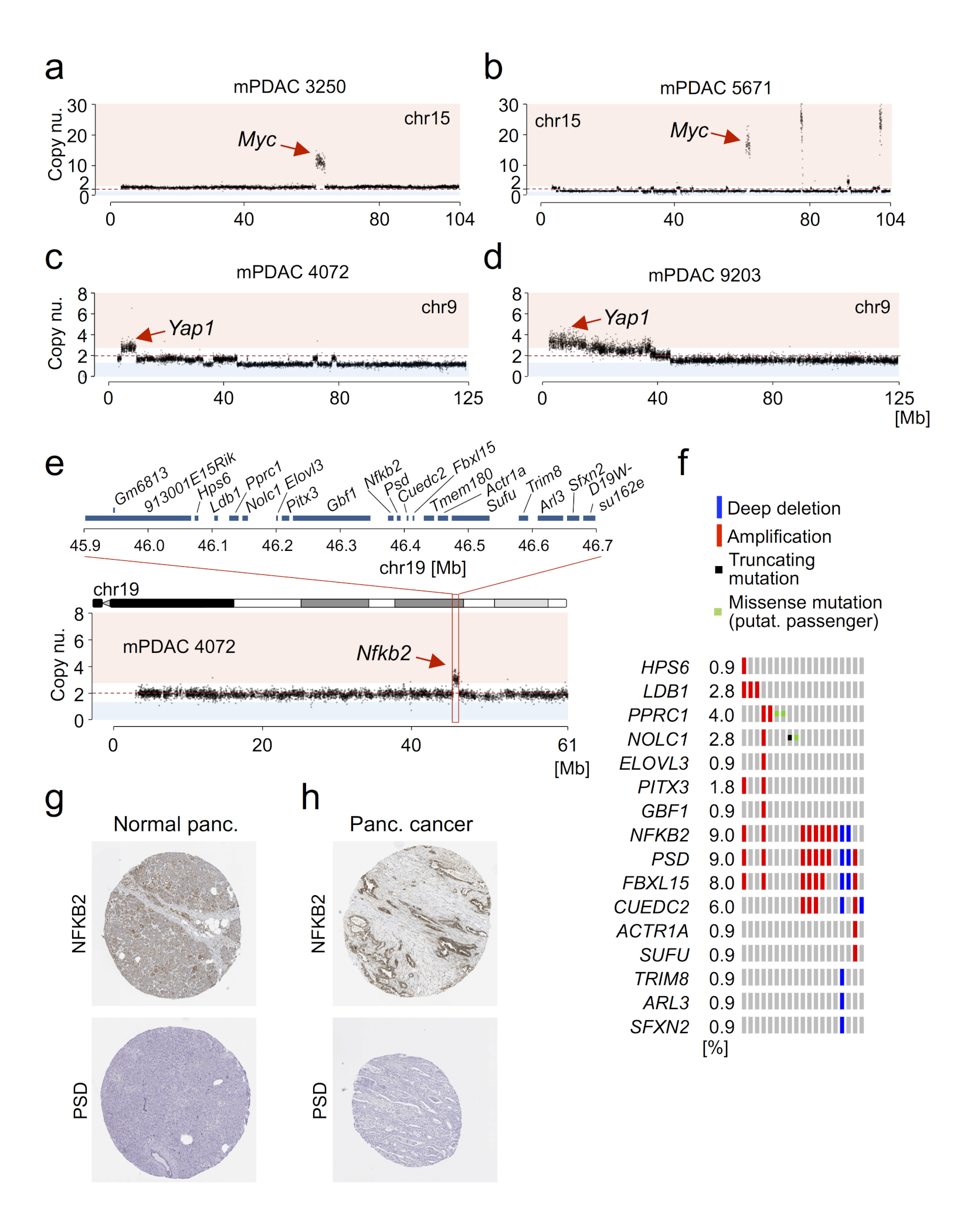
a-b, Two primary mPDACs with strong focal Myc amplification on chr15 are shown, as detected by aCGH. Red dashed line indicates no copy number change. c-d, Focal copy number gains targeting the Yap1 locus on chr9 in primary mPDACs 4072 and 9203 as revealed by aCGH. e, Chr19 was also frequently subject to arm-level gain (see Fig. 1c and Extended Data Figure 1l). Primary mPDAC of PK mouse 4072 harbors a focal gain on chr19 containing 20 genes: 9130011E15Rik, Gm6813, Hps6, Ldb1, Pprc1, Nolc1, Elovl3, Pitx3, Gbf1, Nfkb2, Psd, Fbxl15, Cuedc2, Tmem180, Actr1a, Sufu, Trim8, Arl3, Sfxn2, D19Wsu162e. f, Cross-species analyses revealed that the orthologous region on human chr10 is also subject to recurrent amplifications in human PDAC (8 out of 109 hPDACs have focal amplifications; data from Witkiewicz et al.6). Of the 20 mouse genes, sixteen could be assigned to orthologues in humans. Further analyses revealed that only two genes, NFKB2 and PSD, are within the minimal overlapping region of recurrent amplification (data from6 and oncoplot from cBioPortal60,61). g, NFKB2, but not PSD, shows medium protein expression in exocrine glandular cells of normal pancreatic tissue, as detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC, data from TheHumanProteinAtlas62). h, NFKB2 is highly expressed in 17% (2/12) of stained hPDAC biopsies as shown by IHC. In contrast, there was no PSD expression in any of the analyzed pancreatic cancers (0/12). Protein expression data was used from TheHumanProteinAtlas62.
