Figure 2. Fbx4G is an Atypical Small GTPase Domain without GTP Binding Activity.
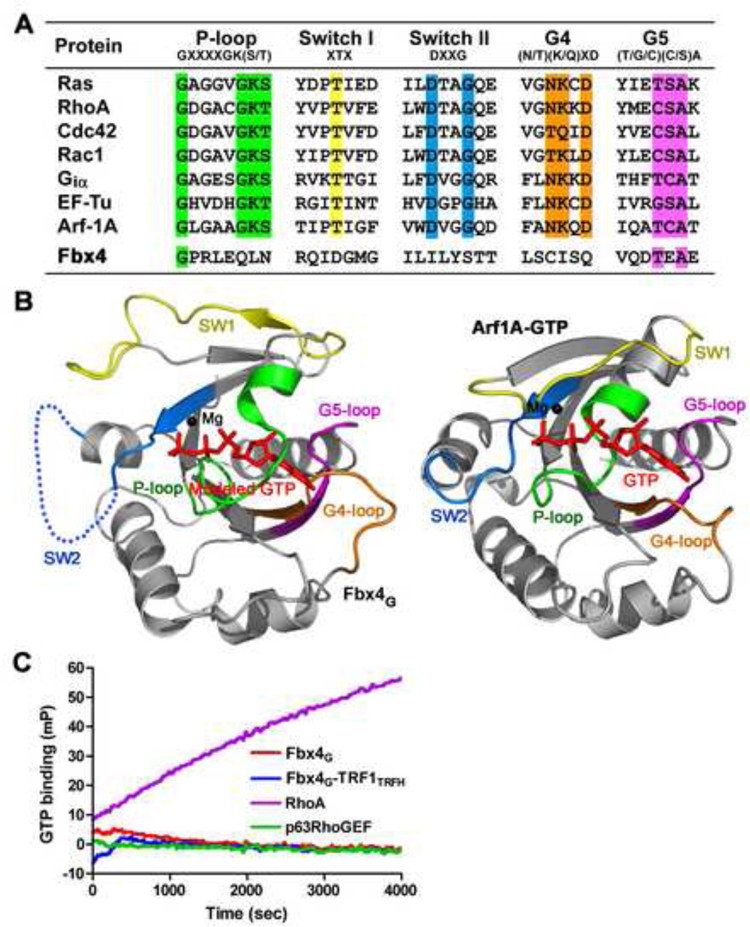
(A) Sequence alignment in the loop regions of Fbx4G and a group of small GTPases. The conserved residues important for nucleotide binding are highlighted in different colors;the P-loop is in green, Switch I in yellow, Switch II in cyan, G4 in orange and G5 in magenta.
(B) The conformation of Fbx4G observed in the crystal structure is incompatible with GTP binding. Left: ribbon representation of Fbx4G with modeled GTP and Mg2+. The Ploop, Switch II and the G4-loop of Fbx4G block the binding of GTP. Right: ribbon representation of the Arf1A-GTP complex (PDB: 2J59). The coloring scheme of the loop regions is the same as in (A). GTP is shown as a stick model and Mg2+ a black ball.
(C) Times courses of GTP binding for Fbx4G and the Fbx4G-TRF1TRFH complex. GTP binding was monitored by the increase in fluorescence millipolarization (mP) of a fluorescent GTP analog as it was bound. In this experiment, neither Fbx4G nor the Fbx4GTRF1TRFH complex bound to GTP. RhoA (a small GTPase) and p63RhoGEF (a non GTPase protein) were used as positive and negative controls, respectively.
