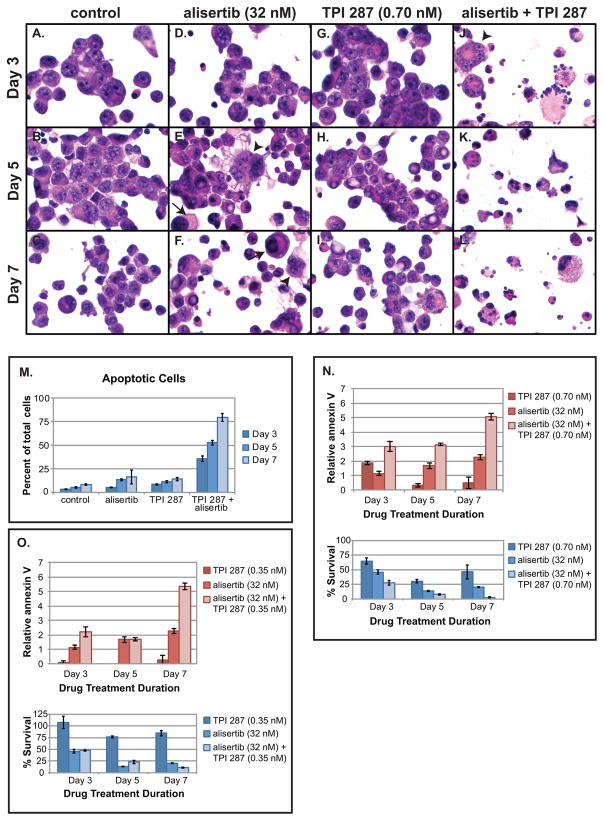
Fig. 2.
TPI 287 and alisertib synergistically induce apoptosis in glioblastoma neurosphere cells. GB30 cells were stained with H&E (A-C) after treatment with alisertib (32 nM, approximate IC50) (D-F), TPI 287 (0.70 nM, approximate IC50) (G-I), or both drugs (J-L) for a period of 3, 5, and 7 days. Arrows indicate large mononucleated cells; arrowheads indicate multinucleated cells. Magnification (600x) is identical in all panels. Apoptotic cells were counted, and average values from 2 experiments are shown (M). Similarly treated neurospheres were dissociated with accutase and counted and stained with an Alexafluor 594 annexin V conjugate and analyzed using a Countess II FL equipped with a Texas Red fluorescent light cube. N. Combined effects of alisertib (32 nM) and TPI 287 (0.70 nM) on apoptosis as measured by fold increase in annexin V binding. O. Combined effects of alisertib (32 nM) and TPI 287 (0.35 nM, 0.5x approximate IC50) on apoptosis. GB30 neurosphere cells showed greatly increased annexin V labeling when treated with TPI 287 and alisertib. This experiment was performed twice and showed similar results. A representative example is shown